Leukemia treatment options in India from the Best cancer hospital in Delhi
Leukemia treatment options in India from the Best cancer hospital in Delhi
- onco
- March 3, 2022
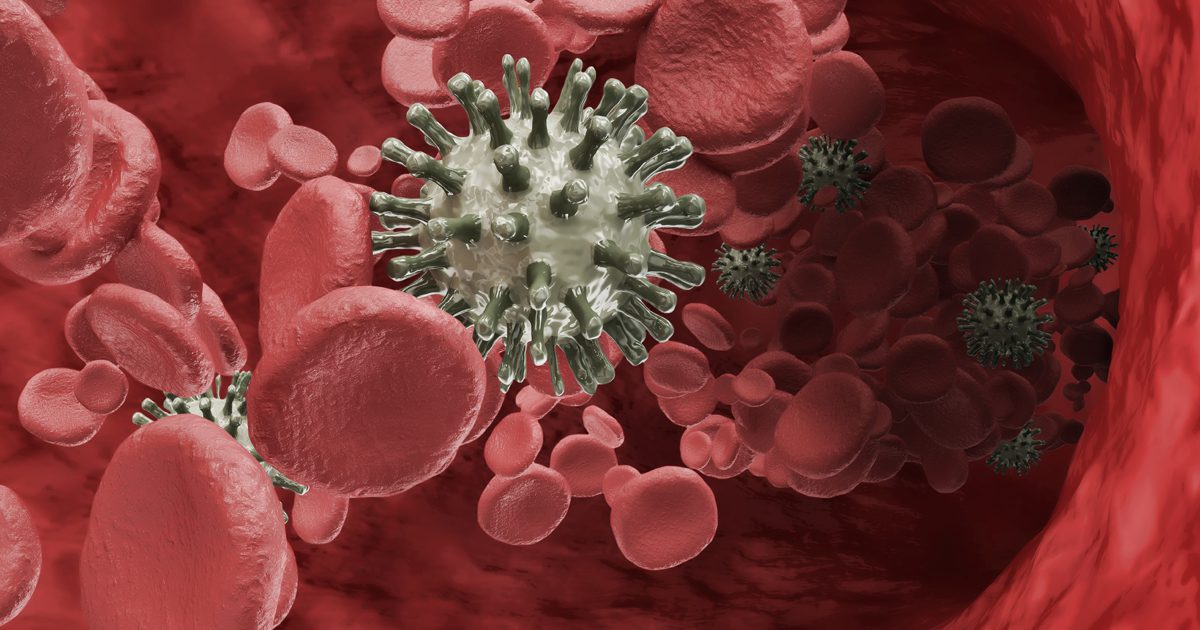
Leukemias are cancers that begin in cells that normally develop into various types of blood cells. Most leukemias begin in the early stages of white blood cells, but some leukemias begin in other types of blood cells.
Acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL) is a type of leukaemia that is also known as acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. The term “acute” refers to the fact that the leukaemia can progress quickly and, if left untreated, will most likely be fatal within a few months. The term “lymphocytic” refers to the fact that it develops from early (immature) forms of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.
Everything begins in the bone marrow (the soft inner part of certain bones, where new blood cells are made). Most of the time, leukaemia cells infiltrate the bloodstream quickly.
LEUKEMIA TREATMENT IN INDIA
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the application of drugs to the treatment of cancer. Chemotherapeutic drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy is therefore useful for cancers that have spread throughout the body, such as leukaemia.
- Targeted Therapy
Drugs used in targeted therapy work by attacking specific parts of cancer cells. They are not the same as standard chemotherapy (chemo) drugs. They occasionally work when chemo does not, and they frequently have different side effects. Some of these medications may be beneficial in certain cases of acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL).
- Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is the use of medications to assist a patient’s immune system in more effectively recognising and destroying cancer cells. Certain types of immunotherapies are now being used to treat acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL).
- Surgery
In the treatment of ALL, surgery plays a very limited role. Because leukaemia cells spread so widely throughout the bone marrow and blood, surgery cannot cure this type of cancer. Surgery, with the exception of a possible lymph node biopsy, is rarely used in the diagnosis of ALL, as this is typically done with a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
- Radiation therapy:
Radiation treatment is similar to getting an x-ray, except that the radiation is much stronger. The procedure is completely painless. Each treatment is only a few minutes long, but the setup time in getting you into position for treatment – is usually longer. The number of treatments you receive is determined by the reason radiation therapy is used.
- Stem Cell Transplant
A stem cell transplant (SCT) allows doctors to use higher doses of chemotherapy (sometimes with radiation) to kill cancer cells. Following the completion of these treatments, the patient receives an infusion of blood-forming stem cells to restore their bone marrow.
- Typical Treatment
Treatment is usually divided into three stages:
- Incorporation (remission induction): The purpose of induction chemotherapy is to put the leukaemia into remission (complete remission).
- Reorganization (intensification): The next phase usually consists of another relatively short course of chemo with many of the same drugs used for induction therapy.
- Maintenance: Following consolidation, the patient is usually started on a methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine maintenance chemotherapy regimen (6-MP).
Recent Posts
-
How to Prepare Yourself for Chemotherapy: Essential Tips and Guidance
November 19, 2024
-
Lung Cancer: Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
November 5, 2024
-
Tomotherapy where precision and efficiency meet health
October 28, 2024
-
What to Eat During Cancer Treatment: Nutrition Tips for Recovery
October 21, 2024
-
Best Blood Cancer Treatment in Delhi
October 8, 2024

Leave a Reply