How precise diagnosis of lymphoma offer patients best treatment options
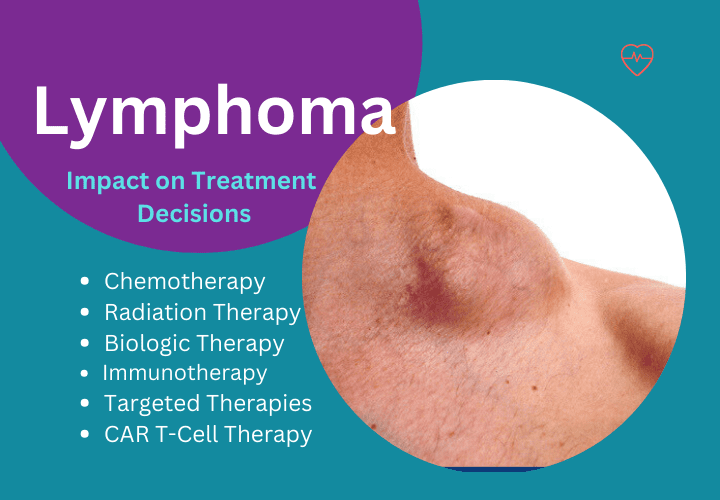
How precise diagnosis of lymphoma offer patients best treatment options
- onco
- April 5, 2024
Lymphoma is a complex and diverse group of cancers that affect the lymphatic system, a critical part of the body’s immune system. Accurate and precise diagnosis of lymphoma plays a pivotal role in determining the most effective treatment options for patients. In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of precise diagnosis in lymphoma and how it impacts treatment decisions and patient outcomes.
Understanding Lymphoma
Before exploring the importance of precise diagnosis, it’s essential to understand the nature of lymphoma. Lymphoma is broadly categorized into two main types: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). These categories encompass numerous subtypes, each with unique characteristics and treatment considerations.
Lymphoma originates from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, and can affect lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen, and other organs involved in the immune system. Symptoms of lymphoma may include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. Given the heterogeneity of lymphoma subtypes, accurate diagnosis is imperative to tailor treatment approaches for optimal outcomes.
Importance of Precise Diagnosis
Identifying Lymphoma Subtypes: Precise diagnosis involves a series of tests and procedures to identify the specific subtype of lymphoma. Distinguishing between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and further sub-classifying into specific types (e.g., diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma) is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Assessing Disease Stage: Diagnostic tests, including imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, PET scans) and bone marrow biopsies, help determine the extent and spread of lymphoma (staging). Treatment approaches vary significantly based on disease stage, with localized disease often treated differently from advanced or widespread disease.
Characterizing Molecular and Genetic Features: Advances in molecular and genetic testing enable oncologists to identify specific molecular abnormalities and genetic mutations associated with lymphoma. This information guides treatment decisions, particularly in the era of precision medicine and targeted therapies.
Diagnostic Procedures for Lymphoma
A comprehensive diagnostic workup for lymphoma typically includes the following:
Medical History and Physical Examination: Gathering information about symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
Imaging Studies: CT scans, PET scans, MRI scans to visualize lymph nodes and detect abnormalities.
Biopsy and Pathology: Removal and examination of lymph node or affected tissue to confirm lymphoma subtype.
Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC), flow cytometry, and other laboratory tests to assess blood cell counts and identify specific markers.
Molecular and Genetic Testing: Advanced techniques to analyze molecular and genetic features of lymphoma cells.
Impact on Treatment Decisions
Precise diagnosis directly influences treatment decisions in lymphoma:
Chemotherapy: Administered either alone or in combination with other drugs to kill cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to recognize and attack lymphoma cells.
Targeted Therapies: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells based on molecular characteristics.
Personalized Medicine in Lymphoma Treatment
Advancements in precision medicine have transformed lymphoma treatment, allowing for personalized approaches that target specific molecular pathways involved in cancer growth. Targeted therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors, have revolutionized the management of certain lymphoma subtypes, improving response rates and reducing side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in the diagnosis and treatment of lymphoma:
Identifying Rare Subtypes: Some lymphoma subtypes are rare and may require specialized diagnostic expertise.
Treatment Resistance: Resistance to targeted therapies and disease relapse pose ongoing challenges that necessitate innovative research and treatment strategies.
Optimizing Diagnostic Tools: Continued refinement of diagnostic technologies, including liquid biopsies and molecular imaging, promises enhanced precision in lymphoma diagnosis and monitoring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precise diagnosis of lymphoma is essential for offering patients the best treatment options and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. By accurately characterizing lymphoma subtypes, disease stage, and molecular features, healthcare providers can tailor personalized treatment strategies that maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects. Ongoing advancements in diagnostic techniques and targeted therapies underscore the promising future of lymphoma management, emphasizing the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration and individualized care in improving patient outcomes.
Recent Posts
-
How to Prepare Yourself for Chemotherapy: Essential Tips and Guidance
November 19, 2024
-
Lung Cancer: Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
November 5, 2024
-
Tomotherapy where precision and efficiency meet health
October 28, 2024
-
What to Eat During Cancer Treatment: Nutrition Tips for Recovery
October 21, 2024
-
Best Blood Cancer Treatment in Delhi
October 8, 2024

Leave a Reply