One of the most prevalent indications of a brain tumor is seizures, especially in those without a prior history of the condition. Epilepsy can have a crippling effect on an individual’s quality of life. Two crippling medical disorders that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life are brain tumors and epilepsy. Treatment choices are essential for people with either of these disorders in order to control the corresponding symptoms and enhance general health. Surgery is one such therapeutic option, and here we will discuss how surgery can benefit patients with epilepsy and brain tumors in this blog post. We’ll also discuss how cutting-edge facilities, like a cancer hospital in Delhi, help cure brain cancer.
Brain Tumors:
Brain tumors are abnormal cell growths that can be either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) within the brain or surrounding tissues. Benign brain tumors do not spread, while malignant brain tumors, often known as brain cancer, can pose a serious risk to one’s life.
Surgery is one of the main methods used to treat brain tumors. When a brain tumor is accessible and safely extractable, surgical excision is frequently advised. In these situations, the operation aims to remove the tumor as much as possible to relieve pressure on the brain and enhance the patient’s general health.
Operation on Brain Tumors:
Brain tumor surgery is a complex and delicate process that calls for a highly competent surgical team. An extensive assessment of the patient’s condition, including the kind, size, and location of the tumor, usually precedes surgery. This assessment aids in deciding on the surgical strategy and degree of tumor excision that is required.
Important surgical methods for treating brain tumors include:
- Craniotomy: During this treatment, an incision is made in the skull to access the tumor. Special equipment and imaging techniques guide surgeons during surgery.
- Endoscopy: To treat some conditions or remove small tumors, minimally invasive endoscopic techniques may be used in certain situations.
- Image-Guided Surgery: During surgery, the surgeon receives real-time direction from sophisticated imaging technologies, such as CT or MRI scans.
- Brain Surgery While Awake: This method is employed when the tumor is close to essential brain regions. To protect vital brain functions, the patient could be kept awake during the procedure.
Epilepsy surgery:
Periodic seizures typify a neurological condition called epilepsy. Epilepsy may occasionally be linked to anatomical abnormalities of the brain, such as brain tumors or scar tissue from infections or head trauma. When medicine is unable to control seizures effectively, surgery may be a good alternative for treating epileptic patients.
Important surgical methods for treating epilepsy include:
- Lobectomy: A lobectomy is the surgical removal of a particular ‘lobe’ in the brain that is the source of seizures. It is frequently applied to focal epilepsy situations.
- Corpus Colostomy: To prevent seizures from spreading from one hemisphere to the other, a corpus callosum (the structure connecting the two hemispheres of the brain) is severed during a corpus colectomy procedure.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): Stimulating the vagus nerve to reduce the frequency and intensity of seizures does not require brain surgery. Instead of this, a device is implanted.
Function of Delhi Cancer Hospital:
It can be beneficial for those with brain tumors to have treatment at a Delhi speciality cancer hospital. These hospitals include cutting-edge infrastructure and a multispecialty team of professionals who can offer thorough therapy for brain cancer.
There are various advantages that a Delhi cancer hospital provides to people with brain tumors:
- Expertise: There are neurosurgeons, neuro-oncologists, and other experts available with a great deal of experience treating brain tumors.
- Modern Technology: These hospitals have state-of-the-art surgical and diagnostic instruments, guaranteeing accurate care.
- Individualized Care: Treatment regimens are customized to meet the specific requirements of each patient, taking into account variables such as tumor location and kind.
- Support Services: Palliative care, counseling, and rehabilitation are just a few of the services available to patients.
- Research and Clinical Studies: Several Delhi-based cancer hospitals are engaged in state-of-the-art research and clinical studies that provide patients with access to cutting-edge therapies.
So, for people with brain tumors and epilepsy, surgery is a vital part of their treatment, providing hope and a better quality of life. For patients to choose the best course of therapy, they must speak with qualified medical professionals. A Delhi cancer hospital can offer patients seeking advanced brain cancer treatment the knowledge and tools required for quality care. And the finest cancer hospital is Oncoplus, which provides a comprehensive approach to controlling and treating brain tumors and epilepsy, thereby improving the lives of individuals affected. We do this by combining surgical skills with the newest technologies and individualized treatment programs. We strive to provide the best possible care to cancer patients, accepting their suffering and enabling them to live happy, healthy lives.
Brain tumors originate in the brain, and it is the abnormal growth of tissue that disrupts the functioning of the brain. Generally, there are two types of brain tumors: malignant and benign. In both tumor types, malignant brain tumors are cancerous and benign brain tumors are non-cancerous. If the patient wants the best cancer treatment in Delhi, they can consult with the oncologist at Oncoplus Hospital. In some people, tumors grow at a very fast rate, and in others, they grow at a very slow speed. The growth of a brain tumor is entirely dependent on its size, location, and type. It is important to note that a brain tumor can affect people of all ages. It is suggested that early diagnosis and timely treatment help fight brain tumors. There are various myths and misconceptions among people about brain tumors that can cause unnecessary fear and confusion. However, it is critical to be aware of the existence of brain tumors. In this blog, you will read about the myths and facts about brain tumors.
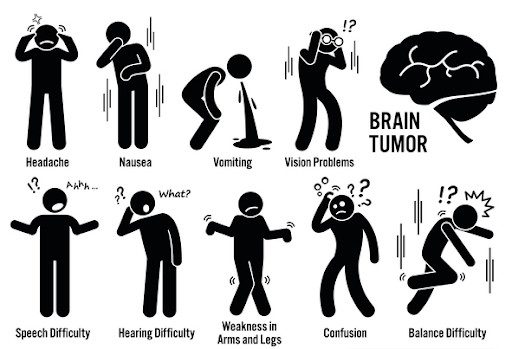
Symptoms of brain tumors:
The symptoms of a brain tumor differ depending on whether it is malignant or benign.
- Headache that occurs early in the morning or if there are changes in the pattern of headaches.
- People might experience different types of seizures.
- If the person is feeling issues in their body, such as loss of consciousness and loss of control over body functions,
- Loss of vision
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in personality or memory
- Fatigue
- Loss of balance
Read More Blog:- Brain Stroke: Warning Signs, Symptoms, And Prevention
6 Brain Tumor Myths and Facts:
Myth 1: Cell phones cause brain tumors.
Facts: There is no scientific evidence to support that the use of cell phones or any other types of radiation causes brain tumors. The radio frequency radiation of these devices affects the skin before it reaches the brain and causes a negative effect on the person’s health. Hence, there is no convincing evidence that the use of cell phones causes brain tumors.
Myth 2: Brain tumors are always dangerous.
Fact: Some of the brain tumors are dangerous, but many of the tumors can be treated and cured with surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, which helps to kill cancer cells. The prognosis for a brain tumor depends on the type of tumor, its location, and the patient’s overall health. Brain tumors are dangerous, but we are treating them.
Myth 3: Brain tumors are always cancerous.
Fact: Not all brain tumors are cancerous. Benign brain tumors have abnormal growths but do not spread to other parts of the body and are typically less aggressive than malignant tumors. These types of tumors are non-cancerous and can be completely treated.
Myth 4: Brain tumors only occur in older adults.
Fact: Brain tumors can occur in people of all ages, including children. In fact, brain tumors are also found in children and newborns in our country.
Myth 5: Brain tumors cannot be prevented by changing one’s lifestyle.
Fact: A person’s lifestyle does not cause brain tumors. By changing your lifestyle, you cannot stop brain tumors from developing. On the other hand, adopting a healthy lifestyle is good for your general health. A healthy lifestyle includes regular exercise, a balanced diet high in fiber, and the refusal to drink alcohol, chew tobacco, or smoke.
Myth 6: Brain tumors always cause severe headaches.
Fact: Headaches can be a symptom of a brain tumor, but not all patients with headaches have a brain tumor. There are various causes of headache, so it should be examined properly. Other symptoms of a brain tumor include seizures, changes in vision, difficulty speaking or walking, and changes in personality or behavior.
In conclusion, brain tumors are a serious health concern, but many myths and misconceptions surrounding them can cause unnecessary fear and confusion. It is important to understand the facts about brain tumors and to consult with a medical professional if you suspect you or a loved one may have any symptoms of this disease. Regular check-ups, early detection, and treatment are the keys to surviving and overcoming brain tumors. At Oncoplus Hospital, patients get the best cancer treatment in Delhi.
Glioblastoma is an aggressive form of cancer that occurs in the brain and/or spinal cord: it is formed from cells known as astrocytes which support nerve cells.
Glioblastoma can happen to anyone at any age, but trends have shown it to occur more in older adults. It can also lead to serious headaches that get worse with time along with nausea, vomiting and seizures.
Glioblastoma, also referred to as glioblastoma multiforme, is very difficult to treat and cure is often not really possible. Our expert cancer specialists are among some of Delhi’s best doctors for cancer treatment, and we admit that it is difficult to treat, but don’t lose hope because treatment can slow down the progress of the cancer with fewer signs and symptoms. Glioblastoma treatment is also uncommon, and some of Delhi’s best cancer hospitals may not be able to provide successful treatment.
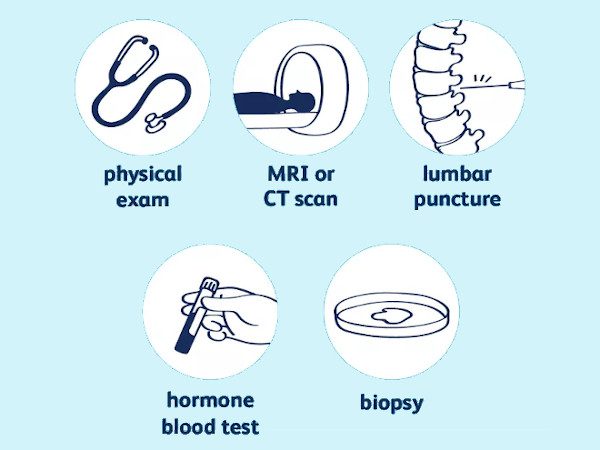
Diagnosis of Glioblastoma
The tests and procedures that can diagnose glioblastoma are:
- Neurological exam. In a neurological exam, your doctor will ask about signs and symptoms, check your vision and hearing, sense of balance and coordination, strength and reflexes. Issues in one or more of these can provide clues about the section of your brain may be affected by a tumour.
- Imaging tests. Imaging tests help your doctor determine the location and size of the brain tumour and MRIs are used to diagnose brain tumours, along with specialised MRI imaging like functional MRIs and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Other include CT and positron emission tomography (PET).
- Taking a sample of tissue for biopsy. A sample of suspicious tissue is extracted and analysed in a laboratory to test the types of cells and the level of aggression the cancer is showing.
These tests of the tumour cells can help doctors determine the types of mutations the cells are undergoing. This can provide some clues to your doctors about your prognosis and could even guide future treatment options.
Treatment of Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma can be treated through:
- A neurosurgeon will remove the glioblastoma and try and remove as much of the tumour as possible. However, as glioblastoma also grows into normal brain tissue, total removal is not possible. To counter this, most will have to receive further treatments post surgery to eliminate the remaining cells.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams like X-rays or protons, to destroy cancer cells and is mostly recommended after surgery and along with chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs for killing cancer cells. In a few cases, really thin, circular wafers that contain chemotherapy medicine are placed in the brain during surgery and the wafers dissolve gradually, at the same time releasing the medicine and killing cancer cells.
After surgery, the chemotherapy drug are taken as pills and is used during and after radiation therapy. - Tumour treating fields (TTF) therapy. An electrical field is used to disrupt the tumour cells’ ability to multiply and TTF involves applying adhesive pads to the scalp which are connected to a device that generates the electrical field.
- Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drugs target and focus on the specific abnormalities in cancer cells that allow them to grow and thrive. The drugs attack those abnormalities, causing the cancer cells to die.
A brain tumour is essentially an abnormal growth of tissue within the brain or in the central spine, this can disrupt and disturb proper brain function. The two predominant types of tumours are, malignant and benign(non-malignant) tumours. Benign tumours are non-cancerous whereas malignant primary brain tumours are cancerous, you should know that less than a third of all brain tumours are cancerous, however, this can occur at any age. The overall incidence of this neurological disorder in India is between five to ten cases per 100,000 people, but ask the best cancer doctors in Delhi and they will tell you there is an increase in incidence. Twenty percent of all brain tumour cases are seen in children and increasing awareness and busting myths can lead to earlier diagnosis and timely treatment.
Symptoms of Brain tumour
The common symptoms that may be caused by brain tumours (malignant or non-malignant) are headaches especially early morning ones that may come with nausea and vomiting. General behavioural and cognitive changes, dizziness, speech and hearing impairment, seizures and paralysis are also symptoms of brain tumours.
Myths and facts of Brain tumour
Brain tumour treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach for treatment and recovery but many misconceptions still remain around brain tumours. We’ll lay out
Some common myths and debunk them with facts on brain tumours:
Myth 1: Brain tumours mean cancer.
- Fact: Only a third of all brain tumours are cancerous and the non-cancerous tumours can be cured through treatment.
Myth 2: Brain tumours happen in the brain, right?
- Fact: Brain tumours occur in the brain, but can also be a result of metastasis of cancer from other parts of the body. The former are called called primary tumours whereas the latter are called secondary tumours which are more frequent than the primary tumours.
Myth 3: Brain cancer won’t happen to young people.
- Fact: Brain tumours have been found to happen at any age; even newborns have been found with brain tumours. Brain tumour is the second most common cancer among children in India.
Myth 4: Brain tumours runs in families.
- FACT : There is still no concrete evidence to suggest this, it’s in fact an older theory which is still unconvincing.
Myth 5: The use of cellphones can cause brain tumours.
- Fact : Again, no research has suggested that phones causes brain tumours but of course, long exposure to radiation might well have severe negative impact on health and should not be taken lightly.
Myth 6: Brain Cancer is common.
- Fact: The chances of a persondeveloping a malignant tumour in the brain is less than 1%.
Myth 7: Changes to lifestyle can prevent tumours.
- Fact:Lifestyle choices do not cause brain tumours and that’s why lifestyle modifications may not really prove helpful in preventing brain tumours. This doesn’t mean making healthy lifestyle choices won’t benefit your overall health; it most definitely will. Regular exercise, a nutritious and balanced diet, staying away from tobacco and alcohol is always a good thing for health.
At Oncoplus Cancer Hospital, our committed team of neurosurgeons, medical oncologists, paediatric oncologists and radiation oncologists specialise in Neurooncolgy to diagnose and treat brain tumours. We are one of the best cancer hospitals in Delhi and use latest in class technology which enables our leading cancer specialists to achieve the highest success and safest resection of all tumours, with the use of novel operative advances with navigation, awake surgery techniques, neurophysiology monitoring with MEP and SSEP.
Brain tumors are cancerous or noncancerous growths in the brain that makes the central nervous system (CNS). Most tumors of the brain are benign this means they are not cancerous and less than thirty percent of brain tumors turn into brain cancer or malignant brain tumors.
Benign does not necessarily mean not harmful. Noncancerous brain tumors can still cause symptoms, noteworthy neurologic problems and damage the healthy brain tissue.
There are two kinds of Brain tumors, they either primary or secondary tumors. Primary tumors begin in the brain tissue itself. Secondary tumors are cancers that have spread, or metastasized, from other areas of the body. For instance, breast cancer normally spreads to the brain. There are more than 100 different types of primary brain tumors that have been identified, they are most common in older adults and children.
Symptoms of Brain tumor differs as per the area of the brain it affects. Symptoms can be very general, such as headache, or very specific, such as changes in the vision. However, specific symptoms, such as fatigue or headaches from a brain tumor, can be common symptoms of other conditions too. The only way to know for sure is to see your doctor for any unusual or insistent symptoms. If your doctor diagnoses a brain tumor, numerous effective treatments are available.
The specific course of therapy will depend on whether or not tumor is cancerous, its location, and how aggressive it is. Slow-growing tumors can cause gradual symptoms that you may not notice for some time. When tumors grow quickly, symptoms can appear rather suddenly.
A few Brain tumor symptoms include
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, swallowing or facial muscles
- Changes in vision, hearing, speech, touch, emotions, and personality
- Weakness, or paralysis
- Fatigue, headache, or head pressure
- Memory problems
- Seizures
- Nausea or vomiting
It’s important to see your doctor if you face of these symptoms that persist or cause concern. Other conditions share many of these same symptoms. Getting a timely diagnosis at Oncoplus Hospitals, Defence Colony, New Delhi, which offers the best chance of successfully treating tumors of the brain.
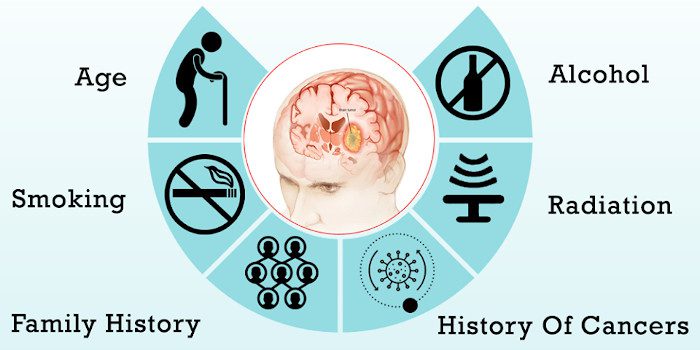
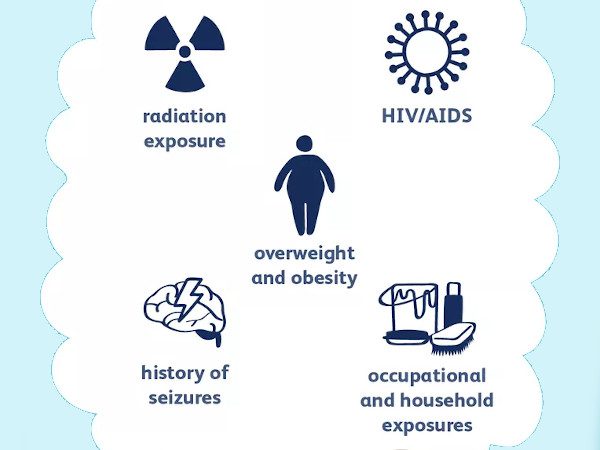
A brain tumor can damage brain tissue and cause problems that may be permanent. Some tumors are more likely to cause problems than others due to their placement in the brain. However, a common concern with any type of tumor is survival. Unfortunately, the risk factors for a brain tumor are normally not changeable. If you have a family history of a brain tumor, talk with Oncoplus Hospitals about your risk and consult about specific monitoring recommendations to find early warning signs. Reducing the risk of a particular disease involves controlling risk factors that you have the power to change.