Cervical cancer is the cause of death among all women. Cervical cancer begins in the cervix’s cells, and the cervix is the narrow end of the uterus. The cervix connects the uterus to the vagina. Cervical cancer grows gradually over time. In this type of cancer, the cervix cells undergo changes, which are termed “dysplasia,” in which abnormal cells start to develop in the cervical tissue. If these abnormal cells are not removed, they will spread rapidly in the cervix and surrounding areas over time. January is cancer awareness month, which is why Oncoplus Hospital raises awareness about cervical cancer, and the best cervical cancer treatment is also available here. In this blog, you will learn about cervical cancer.
Types of Cervical Cancer:
Cervical cancers are of two types: squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Generally, up to 90% of cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas that develop from cells in the ectocervix. Cervical adenocarcinomas, on the other hand, are a rare type of cancer that grows in the endocervical glandular cells and is also known as clear cell carcinoma or mesonephroma.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer:
Usually, cervical cancer is difficult to detect because it doesn’t have symptoms. This is because many women don’t even realize they are suffering from cervical cancer.
In the early stages of cervical cancer, the symptoms that women suffer are as follows:
- When the women have vaginal bleeding after sex or menopause.
- If the regular periods are longer or heavier than normal.
- Women suffer from vaginal bleeding between periods.
- The odor of vaginal discharge is stronger or contains blood.
- If the woman feels so much pain during sex.
In the advanced stage of cervical cancer, the symptoms that women suffer are as follows:
- If there is a pain in the bowel and bleeding from the rectum,
- When a woman experiences pain while passing urine or when there is blood in the urine.
- If a woman experiences abdominal pain or fatigue, consult the doctor.
- Or if there is swelling in the legs.
Factors That Increase Your Risk of Cervical Cancer:
- If a person has a weak immune system, then their body cannot fight HPV infections.
- If the person smokes or breathes in secondhand smoke, this will also increase the risk of cervical cancer.
- If the person becomes sexually active before 18 years of age or if they have multiple sexual partners, then they have a high risk of HPV infections.
- Cervical cancer also occurs in those who use oral contraceptive pills or give birth to many children.
Methods for Preventing Cervical Cancer
According to your age, health, and lifestyle, cervical cancer occurs in women. But some precautions can be taken to prevent cervical cancer. The precautions are as follows:
- Get vaccinated against HPV infections.
There are vaccines available for both adults and young children to protect against HPV infections. It is essential to give the vaccine to a person before they are exposed to HPV. This vaccine will help prevent cervix cancer. Usually, the side effects of this vaccine are mild, such as redness, soreness, and swelling at the injection site. HPV vaccination is recommended for children between the ages of 9 and 12. This vaccination is not recommended for those who are older than 26 years of age.
- Regular Pap Tests:
The Pap test is the best test for the early detection of cervical cancer, and it is also known as a Pap smear. A Pap test can also be combined with an HPV test.
- Visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA):
VIA is a test that is done with a few tools and also with the naked eye. In this process, white vinegar is applied to the cervix. The doctors then observe the abnormalities on the cervix, which turn white when exposed to vinegar.
- No Smoking:
To protect yourself from cancer, you should not smoke, as smoking leads to squamous cell cervical cancer.
Treatment for Cervical Cancer Is Available:
The treatments that are available for cervical cancer are surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. These treatments help kill cancer cells.
Everyone should discuss cervical cancer with their doctors and choose an appropriate screening test as a precaution. Screening tests are recommended for people in their early teens, especially those who are at high risk of developing cervical cancer. Oncoplus Hospital is the best cancer hospital in Delhi for cancer patients.
HPV (Human papillomavirus) refers to a group of more than 200 viruses, and some of these can spread via vaginal, anal, or oral sex: these are sexually transmitted HPVs and they fall into two categories
- Low Risk Human papillomavirus don’t cause any disease but very few low-risk HPV types can cause warts around the genitals, anus, throat or mouth.
- High Risk Human papillomavirus cause several types of cancer and there are about 14 high-risk HPVs out of which HPV16 and HPV18 cause most HPV-related cancers.
HPV infections are common and almost all sexually active people do get infected with HPV within a matter of months to a few years of becoming sexually active and about half of these infections are a high-risk HPV type.. Both men and women can get infected with HPV and develop HPV cancers.
Most HPV infections will not cause cancer as the immune system controls HPV infections so they don’t end up causing cancer.
High-risk HPV infections that remain can cause cancer as HPV infections may not be successfully controlled by the immune system. When a high-risk HPV infection remains for many years, it can cause cell changes that, if left untreated, can get worse with time and turn into cancer.
Getting an HPV vaccination can prevent cancer as they prevent infection with disease-causing HPV types, and prevent HPV-related cancers.
If you’re considering treatment for HPV cancer in Delhi or wish to consult the best oncologists in Delhi, you can read on or reach out to us.
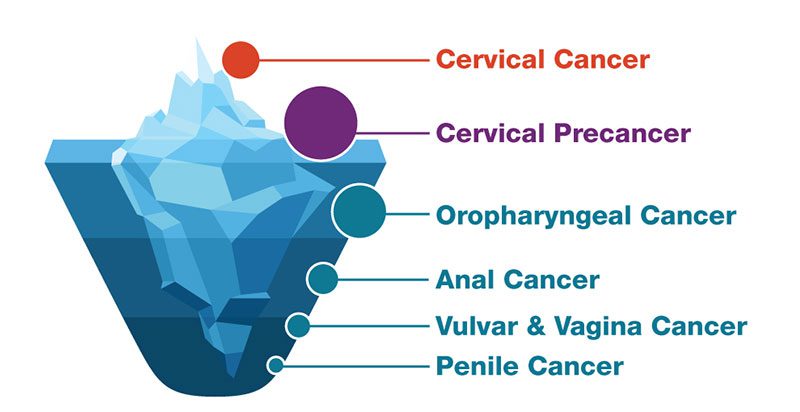
The types of cancer HPV can cause are:
- Cervical Cancer- did you know that all cervical cancers are actually caused by HPV? Routine screening can treat most cervical cancers by allowing doctors to find and remove any precancerous cells before they develop into cancer.
- Oropharyngeal Cancer- Most of the cancers develop in the throat are caused by HPV.
- Anal Cancer – almost 90% of anal cancers are caused by HPV with more of cases and deaths from anal cancer increasing each year. Anal cancer is nearly twice as common in women.
- Penile Cancer- almost all penile cancers (over 60%) are caused by HPV, it is arare type of cancer.
- Vaginal Cancer-almost three fourths of all vaginal cancers are caused by HPV, these are rare as well .
- Vulvar Cancer- seventy percent of vulvar cancers are caused by HPV.
HPV VACCINE
The HPV vaccine helps protect against infection from nine HPV types: two low-risk HPV types that cause most genital warts, plus the seven high-risk HPV types that cause HPV-related cancers.
HPV vaccination is recommended to avoid new HPV infections and HPV-associated cancer, among other diseases.
Vaccination prevents but cannot cure an infection and the HPV vaccine is not meant for treating HPV infections or diseases caused by HPV. HPV vaccination is most effective when given at ages 9-12 and can prevent up to 90% of HPV-related cancers.
Get HPV Vaccine from Best Hospital in Delhi
Who can get the Human papillomavirus vaccine?
The HPV vaccine series is recommended for girls and boys, at the age of 11 or 12, and the series of vaccines can be begun at age 9. It is important for both males as well as females to get vaccinated, because both men and women can develop HPV cancers
The vaccine can also be given to adults between the ages of 27 and 45 who didn’t get the vaccine earlier. Adults in this age group will benefit less from the vaccine because they are more likely to have been exposed to HPV already.
If you’re looking at HPV cancer treatment in Delhi or NCR, or have gone through treatment and want a second opinion, feel free to contact us, and we’ll be with you right away.