Coping with a cancer diagnosis: Emotional & psychosocial effects
A cancer diagnosis is a life-changing event in anyone’s life. It is a destructive disease-causing vita psychological problems among the patients and their family and friends. Psychological agony is a significant and continuing problem for those suffering from cancer who are heavily affected by the time of diagnosis, in the first year after the diagnosis, and commonly during their treatment.
Their mental health needs should be handled with care, but are often ignored as they are not always properly recognized and understood. In the past ten years, there has been a growth in implementing and spreading screening methods for the psychological outcomes of cancer, including depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress, isolation, hopelessness, distress, and demoralization. Also, guidelines and agencies dedicated to the management of the psychological consequences have been developed and supported by several scientific cancer associations.
Physiological consequences of cancer
By just hearing the word “cancer” said the doctor can have a major effect on a person’s mental and physical health, and relationships with our loved ones. While treating the physical consequences, patients should not ignore the emotional issues related to cancer. One can improve their life by learning more about cancer which may help to make the disease seem less frightening and mysterious.
A patient’s financial, psychological, and social situation may all change due to cancer and its treatment. Here are some of the most common mental effects on a cancer patient:
- Reduction in the performance and functional activity, poor memory, and concentration, disrupting sexual activity are important in influencing the physiological response of cancer patients.
- The loss in the stability of one’s emotional position( e.g. anxiety, fears, sadness, and worries), the reduction in self-esteem, the need for dependence on others, and feeling hopelessness is often experienced by the patients. The change of certainty about the future is also an example of emotional effects during this illness. This also includes the changing whole set of personal values, about our importance, questioning the meaning of one’s own life and existence.
- Social intercourse and skills, communication between the family, and close relationships are also affected by cancer.
- Feeling of sadness, loneliness, abandonment, panic, problems in returning to work, or even hiding their medical condition from others are common issues related to cancer patients.
- The most common effects of this diagnosis are mental disorders including major and minor depression, stress and adjustment-related issues, anxiety disorders, emotional distress, sexual disorders, and demoralization syndrome.
All of these aspects may be shown in the different phases of the disease from diagnosis to treatment or medical care. Patients tend to adopt variable emotional, cognitive, and behavior toward the disease.
Consequences of physiological problems and disorder
Psychological distress and disorders have magnificent negative effects on the patients and even on their families and loved ones.
- Cancer patients experience huge levels of cancer-related disorders which may heavily affect their health, quality of life, and the chance of survival in a negative way.
- Distress involves a range of feelings from endangered to sad to depression, anxiety, isolation, hopelessness, and panic. But importantly, general severe distress has an impact on cancer evolution.
- This type of distress results in disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and activating the sympathetic nervous system that has a devastating impact on the cardiovascular immune and the endocrine systems.
- These disturb the biological activities such as catecholamine production, changes in circadian cortisol levels, cellular immune suppression, activation of proinflammatory cytokines, and regulation of leukocyte and tumor cell gene expression, that can promote cancer growth and spread of cancerous cells in a different part of the body.
- An increased rate of suicide is also associated with cancer.
TLS usually develops within a few hours to 2-3 days after the start of the chemotherapy. The mortality rate of patients suffering from tumor lysis syndrome is less the 20%
Care and Treatment
Attend support groups
A good social support network has always been associated with an increased and improved quality of life for those patients who are suffering from cancer and undergoing treatment and its distress. Knowing about cancer can make the patient feel less scared and more empowered. Nearly all studies have shown an improvement in physiology for cancer, attending support groups. Social groups help patients in reducing their pain and anxiety.
Routine screening
Screening should be part of care and clinical practice guidelines, these were developed a few years ago and are extremely helpful to clinicians in providing wide-ranging care for cancer patients and their families.
Converse with your doctor
The patient should try to talk openly with the doctors, one of the main reasons why the doctors are unable to distinguish between the general sadness and the severe distress as the patient doesn’t talk openly to the doctors or their caretakers. One-third of cancer patients experience severe distress but about 5-6% can get through it. There is no shame in sharing the problems openly and asking what you need and lack.
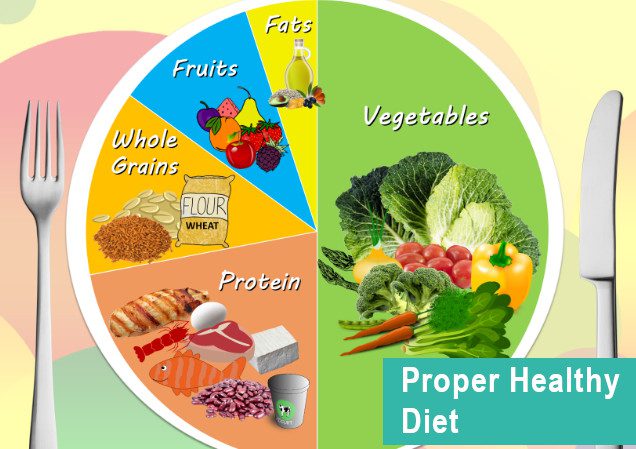
Proper healthy diet
Patients should be provided with a healthy and nutritious diet, these improve the physical condition of their body exercise, when possible is important. Studies show that this helps to keep the mind calm, improving memory and concentration, and strengthens the body. This also allows the patient to spend time with others.
Express your feelings
It’s okay to feel a certain way at a point in your life. But it’s also healthy and common to express how you feel to your loved ones. Don’t fear expressing strong feelings like anger or sadness, let go of them as much as possible. Talk about your feelings to a close member of your family or friends, or with other cancer survivors and support groups. If you still find it difficult to discuss your condition with others, express your feelings by thinking about why you feel them or write them down.
Quit blaming yourself or plead guilty
You are strong and brave. Don’t let any condition weaken your spirit and question your mental health. Most cancer patients tend to blame themselves for getting cancer. Although it’s completely incorrect, even scientists don’t know how a person gets cancer and how someone else doesn’t. All bodies are different and cancer can happen to anyone, from a triathlete to a programmer. It’s not up to us.
Dominate the positive, over the negative
It’s always easy to come across a negative when a condition worsens or you are under a problem. It might sound cliche, but life has both dark and light moments. Try to look for the good part of all things even in a bad time or be hopeful rather than thinking the worst. How we perceive the world, the world also becomes the same for us. So try to focus your energy on getting better, and staying healthy as much as possible. Express love to your loved ones for being there with you in misery and fortune. When you start to think of the good, you’ll get many reasons to be happy about in life.
Be in Incharge of things
Just because you’ve got cancer doesn’t mean you are helpless. You can completely control and take charge of your life like you did before. Stay involved in your health care, try to learn about the medicines, keep up with your appointments and make good lifestyle changes to turn things better accordingly. Scheduling your day daily is a power move, it gives you a great sense of control. Not just physically, controlling your thoughts can help. Although you can’t control every thought, try not to think about the worse or fearful ones, instead try to look up for the positive things like someones’ birthday, anniversary, next picnic, or a good book.
Don’t pretend, feel free to feel down
Don’t try too hard to follow the rules as well. Staying positive and thinking for the best is an ideal way to live but it’s completely normal to feel sad or gloomy once in a while. Have freedom over your feelings.
Decide when you want to discuss cancer
Cancer is still very unknown to people and often they tend to talk to you about your conditions. It can be overwhelming and tiring to discuss cancer so frequently with every relative or well-wisher you meet. Even when the loved ones mean well, you must let them know what and how you feel about the subject. If you don’t want to discuss them, politely express to them that you are not comfortable talking about them.
Rely on a long-lost hobby
Hobbies are always fun to explore. Bring back your old hobbies such as woodworking, reading, art & crafts, paintings, photography, or watching movies, listening to music, or dancing all night. Look for things to enjoy with kids in your family, take your mind off on a fun and interactive tasks.
Enjoy Solitude
Relaxing by yourself or doing an activity that helps you unwind and enjoy silence can be a great escape from the chaos that comes with cancer. Try to do relaxing activities such as meditation, exercises, guided imagery, and others to help your body and mind relax and release stress.
Stay Active
Don’t just lie on your bed all day. That won’t help with anything in life. Getting out of your house and going for a little jog, or doing exercise or gentle yoga can keep you fit and active.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Guide to Tumor lysis syndrome: Vital things to know
What is tumor lysis syndrome?
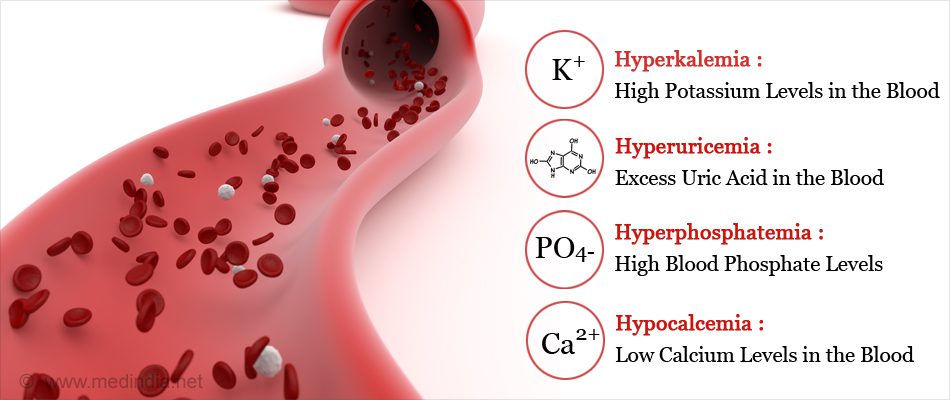
Tumor lysis syndrome ( TLS ) refers to the condition of metabolic disturbance which occurs when a large number of tumor cells or neoplastic cells are killed briskly within a short period, leading to the release of intracellular components in the blood. This syndrome is characterized by the quick development of hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, with acute kidney injury and is hazardous.
TLS is common in people having blood-related cancer and lymphoma( lymphatic cancer). It initially rises through chemotherapy. Risk factors include tumors with rapid cell growth and movement, hematologic cancers like acute leukemia, or tumors with a high sensitivity to chemotherapy.
Patients with high levels of lactate dehydrogenase (greater than 1,000 U/L) and people with damaged renal function are also at risk. Various chemotherapy agents like cisplatin, etoposide, cytarabine, and paclitaxel are also connected with this syndrome.
How does it develop?
Not all cancer patients have an equal rate of developing this syndrome. TLS is most likely to happen when blood disorders and cancer are treated with chemotherapy. In highly reproducing cancer acute leukemia, few cells die before the treatment as it’s the end of their life cycle.
If a huge amount of these cells lyse and die, TLS may grow before the beginning of the treatment. However, a huge amount of intracellular substances are released in the bloodstream as most of the neoplastic cells in the bone marrow and bloodstream of patients suffering from acute leukemia are destroyed through chemotherapy.
These cells get destroyed and die, a large amount of phosphate and potassium are released including purine nucleic acids.
Patients with huge “tumor burdens” (number of cancer cells in the body) or have rapidly dividing cells that respond well with treatment are at high risk. These include:
- Leukaemia
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Tumors like hepatoblastoma and neuroblastoma
- Myeloproliferative diseases or neoplasm
- Cancer that causes the ill function of the kidney before the treatment start
Other risks
- Intrathecal chemotherapy ( injection of chemotherapy, given directly into the fluid-filled space around the brain and spinal cord).
- Chemoembolization ( soothing treatment for tumors found in the liver).
- Radiation therapy (uses a beam of huge and intense energy to kill cancer cells)
- Corticosteroid therapy
- Hormonal and biological therapy
TLS usually develops within a few hours to 2-3 days after the start of the chemotherapy. The mortality rate of patients suffering from tumor lysis syndrome is less the 20%
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of these syndromes may be lenient at first, but become hazardous over time due to the mixing of several substances in your systemic circulation. Symptoms of TLS include:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Weakness and fatigue
- Numbness, seizure, and tingling
- Muscle cramping and joint pain
- Hallucinations and confusion
- Decreased, dark urine
If TLS left untreated, it eventually leads to severe outcomes, these include:
- Seizures
- Abnormal heart rate
- Loss of muscle control
- Even death
Hyperkalemia, Hyperphosphatemia, Hypocalcemia and hyperuricemia
Generally, the first sign of TLS is hyperkalemia and the most dangerous component of this syndrome as potassium tends to leave the cell before they rupture. Hyperkalemia is defined as a medical condition of the body when it has too much potassium in the blood. Potassium is an important nutrient and helps in building nerves, muscles, and the heart.
Mild hyperkalemia is usually asymptomatic but chronic ones can cause a threat to life, cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, or paralysis. This electrolyte can cause lethal dysrhythmias and damage normal cardiac functions. The kidneys aren’t able to excrete enough potassium to remunerate for the hyperkalemia as it is submerged by excess potassium.
Hyperphosphatemia is known as having a high level of phosphate in the blood released from the cancerous cells, phosphate is an electrolyte i.e. electrically charged substance that has phosphorus in it. The kidneys try to get rid of the excess amount of phosphorus in the bloodstream by increasing urine output and decreasing the amount of phosphorus reabsorption, but in the end, it reaches its limits where they can no longer payback, and phosphorus piles up in the blood. Generally, Hyperphosphatemia develops 1-2 days after the treatment.
As phosphate levels increase, phosphate ions (negatively charged) merge with calcium ions (positively charged) eventually leading to decreased serum calcium level. A condition where the body has really less than enough calcium is known as Hypocalcemia. It is also a sign of TLS. These calcium-phosphate complexes cause tubular obstruction and acute renal damage.
Neoplastic cells also release purine nucleic acid. Usually, purines are metabolized to hypoxanthine, converted to xanthine, and then to uric acid by the enzyme xanthine. An excess amount of purines are released rapidly in the blood during this syndrome. The kidneys are unable to excrete the overwhelming amount and results in hyperuricemia and uric acid formation in the kidneys. Hyperuricemia is seen 48 to 72 hours after the beginning of chemotherapy.
Due to these circumstances, the kidneys are submerged by excess phosphorus, potassium, uric acid crystals, and calcium phosphate precipitate leading to acute renal failure. The kidney tries to compensate for the increased electrolyte and uric acid by increasing the urine output, but can’t, due to uric acid nephropathy and volume depletion.
Lab work is carried out every 6 hours for the first 24 hours after chemotherapy started if a patient is in danger due to tumor lysis syndrome.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs, lab tests, and symptoms are used in diagnosing the tumor lysis syndrome.
The Cairo-bishop grading system, used in classifying and grading TLS, states lab anomalies in serum uric acid, phosphorus, potassium levels 25% increased over baseline, and serum calcium levels were decreased by 25% from baseline.
This system contemplates lab value alters that occur in patients from 3 days before to 7 days after the beginning of chemotherapy. The lab irregularity organized by the system is categorized based on cardiac dysrhythmias, seizures, severity including age-adjusted serum creatinine.
Tumor lysis syndrome is generally diagnosed by:
- Complete blood cell count
- Phosphorus and calcium test
- Urinalysis
- The uric acid level in the blood
- Creatinine level
Quick identification key
One can recover from this life-threatening problem of cancer treatment if they are promptly able to recognize the signs and symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome and take preventive measures.
Prevention and treatment of TLS
To help prevent TLS, the following steps you should be taken:
- Before the beginning of treatment, your healthcare will determine whether you have the risk of developing this syndrome. This is based on the type of cancer.
- Lab tests, checking conditions like poor kidney function, heart disease, or hypertension
- Medications like Allopurinol ( Lopurin, Zyloprim (Aloprim) should be taken, to reduce or stop the amount of uric acid and rasburicase (Elitek, Fasturtec) for breaking down the uric acid.
- The level of electrolyte should be balanced
- Level of calcium and potassium
Allopurinol
It stops the conversion of xanthine to uric acid and hypoxanthine to xanthine by inhibiting xanthine oxidase. Ideally, it starts 1-2 days before the starting of chemotherapy.
Monitors patients for any fever, allergies, or skin rash including nausea, vomiting, and chills. Common unfavorable results from the intake of allopurinol headache and drowsiness.
Allopurinol therapy is done before chemotherapy as it helps to prevent excess uric acid. It has no effect on patients suffering from hyperuricemia and it increases the level of xanthine that could damage the kidney.
It is never operated with capecitabine because allopurinol may deteriorate its effectiveness.
Rasburicase
Rasburicase is a drug that cures hyperuricemia, changes uric acid to allantoin. allantoin is more soluble than uric acid in urine. This drug decreases the level of uric acid and manages the amount of serum potassium, calcium, phosphate, and creatinine.
Also, it works quickly and takes 4-5 hours to show effectiveness. Patients should be well hydrated before taking this drug. Patients with large tumor burdens tend to take longer therapy (up to seven days or twice/day) while for other patients it is effective in 1-2 days.
Pay attention to the patient taking rasburicase while sending lab specimens for the uric acid level test. To maintain approx uric results, the blood samples must be kept on ice after being taken. Poorly ensured samples will give false results because any uric acid of the sample being reduced by rasburicase at room temperature.
Patients receiving this drug should not be supplied with allopurinol as it can interfere in the work of rasburicase and may decrease its effectiveness. Rasburicase should never be given to patients suffering from glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency due to the risk of critical hemolysis.
Stop giving this drug to the patient if it shows a sign of hypersensitivity. Signs of hypersensitivity reactions include bronchospasm, urticaria, dyspnea, chest discomfort, hypoxia, and hypotension. The most common unfavorable reactions of patients related to one dose of this drug infusion are headache, vomiting, and fever. But eventually results in urticaria pruritus, dyspnea, increased liver enzymes, and chest and back pain with increased or repeated dosing.
Healing the complications of TLS
- Patients with TLS should be provided with enough water and stay well hydrated before the treatments.
- IV calcium should not be delivered to patients with hyperphosphatemia, because it increases calcium phosphate precipitation.
- Hyperphosphatemia control is managed with phosphate binders such as aluminum hydroxide given in limited dosages to avoid aluminum toxicity. Other phosphate binders having calcium, such as calcium carbonate or calcium acetate may be used instead.
- Ensuring the sign and symptoms of hypomagnesemia from sodium sulfonate and hypocalcemia using sorbitol also the patient’s 12-lead ECG should also be monitored and maintained as it plays a role in indicating and accessing cardiac rate and rhythm for dysrhythmias.
- Patients having symptomatic hyperkalemia should be accessed with iv regular insulin and dextrose for redistributing potassium, within the cell.
- Patients not responding to these measures should be accessed to a renal replacement, such as hemodialysis, to manage renal failure and electrolyte anomalies.
Quick identification key
One can recover from this life-threatening problem of cancer treatment if they are promptly able to recognize the signs and symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome and take preventive measures.
Cautious of these medications!
A list of medication, patients suffering from TLS must avoid or there would worsen the effects of this syndrome:
- Acetylsalicylic acid,(aspirin)
- Medication containing potassium and phosphorus
- Beta-blockers
- Mannitol
- Some antibiotics
- Heparin
- Bisphosphonates
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
- Nephrotoxic agents such as aminoglycosides and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Effects of Covid-19 on Cancer: Here’s what you must know
Covid-19 has shaken the world around us. In these unprecedented times when there’s danger from every side, being a cancer patient can be terrifying. Many cancer patients have suffered from a higher risk of coronavirus due to their withering immunity system. The growing fear, anxiety, and unawareness have taken a toll on everyone’s life, not just on people with cancers. However, we are in this together and united, we can make each other’s life a lot better.
Today, we’ll uncover all the essential information you need to understand between COVID-19 and cancer. And the impacts of covid-19 on cancer patients, caregivers, and treatment options we can take to uncomplicate things.
What is coronavirus?
After reading thousands of articles each claiming to hold new data about this newborn fatal disease, coronavirus isn’t a mystery anymore. It’s an infectious disease caused by a new type of coronavirus. A coronavirus is a group of viruses, each causing some or other health problems. Some cause cold, and flu while the other result in severe damage to breathing or respiratory systems. Depending on your immunity, the virus can or can’t hinder your health.
The most prominent factor of this deadly disease is that it’s contagious, spreading from person to person. It spreads through a sneeze, cough, or by talking or singing loudly. Any type of physical contact with a coronavirus-positive person can lead to spreading to you.
How risky is covid-19 for cancer patients?
Covid-19 isn’t a piece of good news to anyone, especially not for people with cancers. You are at a higher risk of getting covid-19 if you suffer from cancer. It has a lot to do with the weakened immune system resulting from cancer. Our immune system is highly essential for the protection of the body from foreign damage like viruses, bacteria, and other germs. It battles out numerous infections, and diseases if the immunity is powerful.
More than 89 cancer patients have been subjected to ICU due to covid-19 with a mortality rate of 36%, according to Michael Dang, MD at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. However, there’s a ray of hope, cancer with coronavirus is SURVIVABLE.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19 with cancer?
The symptoms of COVID-19 to a cancer patient are nothing sort of different from the general population. Here are the symptoms associated with cancer:
- Increase in body temperature than 37.8C
- Extreme and continuous coughing (Lasting more than 3 to 4 hours)
- Loss of taste and smell
- Fever and fatigue
- Trouble in breathing
If you notice such symptoms in your body, then immediately contact your chemotherapy helpline or the oncology service.
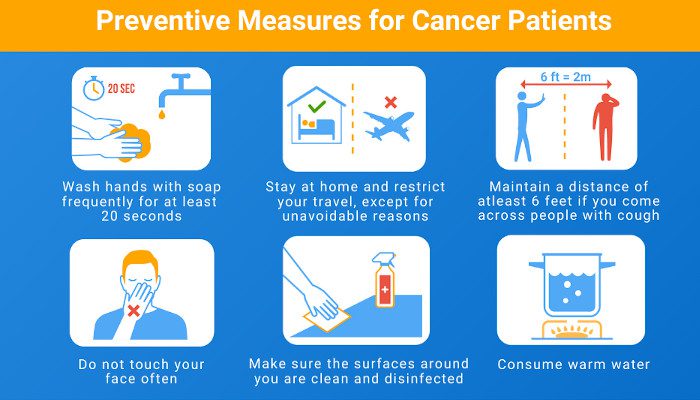
What are preventive measures against COVID-19 as a cancer patient?
Cancer patients at a higher stage or the most vulnerable ones are extremely at great risk of developing COVID-19. Known as the most vulnerable group. If you identify with it, then as per the government instruction, you must take special preventive measures to ensure your health and immunity strength.
People who are the most vulnerable includes:
- Undergoing chemotherapy
- Undergoing radical radiotherapy for lung cancer
- Suffering from bone marrow cancer like leukemia, myeloma, and lymphoma
- Undergoing targeted cancer treatments that affect the immune system, like protein kinase inhibitors or PARP inhibitors.
- Enduring immunotherapy or continued antibody treatments for cancer
- Gone through bone marrow or stem cell transplants in the last 6 months or prescribed immune suppression drugs.
Vital everyday precautions to take
Wash your hands: Cleanliness must be the top priority against the covid-19 spread. Regularly wash your hands and at consistent hours. Don’t use soaps, use the hand wash bottles as it’s a much cleaner and safer option. Wash your hands for at least 20 seconds each day and finish it by using a sanitiser.
Avoid Touch: Get rid of touching your face, nose or eyes, as much as it is possible. Public places and areas are equally contagious, like the metro, bus, auto or restaurants while things like elevators, doorknobs require touching, so try to limit it.
Maintain distance: The two meters of long-distance must continue for a long period. Despite it’s at home or a workplace, coming in close contact with anyone can promote the spread of the disease.
Stay Indoors: We can understand the quarantine period was extremely exhausting, both mentally and physically. But to overcome the global pandemic, we must continue staying indoors while protecting each other. So, cancel all non-importance travels and tour plans including your holidays to prioritize your health and safety of others.
Wear a mask: Nothing’s more important than sealing the entrance of the viruses entering your body – the mouth and the nose. You must wear a mask that covers your mouth and nose, properly while stepping out for mandatory work.
How to manage cancer screening in COVID-19?
The onset of COVID-19 forced various medicare centres to shut. It resulted in a great reduction in cancer screening all this while. Even mandatory measures like cancer screening have ceased to reduce the risk of coronavirus spread among each other. Although for good cause, screening must be done. Fortunately, with things dissolving back to normal and businesses are reopening along with less restriction, you can visit places to do a cancer screening test.
If you’ve missed your screening test then reschedule or talk to your healthcare professionals for better timing. Discussing with your healthcare provider, over a phone call or video chat indicates the risk and benefits of getting a screening in the current environment. Depending on the situation of people and calculating the risk to step outside, helps to decide if you’d want to postpone it or not.
Be careful about your decision as cancer screening is a life saviour, it’s important to get a checkup. Not right now, but after a while, opting for cancer screening must be your top-most priority.
FAQ’S on Cancer in times of COVID-19
If you had cancer and got treated, is there still a risk from COVID-19?
Globally, the only threat to billions of lives is the coronavirus, no matter what weight, race, gender or country you are from. People with cancer are at great risk of getting Covid due to their weakened immunity from cancer and it’s treatment.
If your cancer treatment is complete, then your immune system would take time to recover from its weak condition. People who’ve suffered from cancer in history, are equally, in fact extremely vulnerable groups to acquire COVID-19.
What to do if you’ve symptoms of Covid-19, as a cancer patient?
If you notice similar symptoms of COVID-19 in your body, then reach out to your treatment of cancer or oncologist to report and state your condition. There’s no need to panic or worry. Once the doctor comes to know about your situation, you’ll be recommended with the right solution tailored to your needs.
Should I hurry or wait for cancer treatment in the pandemic?
The answer to opting or delaying cancer treatment depends on your situation. Discussing and calculating the risk of COVID-19 with the risk of cancer progression would paint a bigger picture of the importance of seeking treatment. When you weigh the risk and benefits of your situation, treatment timing won’t be a problem anymore.
While calculating the risk, your cancer diagnosis, health, and age play a major factor. If you’re an older adult, that has a slow progression of cancer, then holding off the cancer is a sensible decision, only if you have a communal spread of the virus. But, if you’re much younger and have aggressive cancer development then immediate treatment is the right decision.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
What you must know about cancer in children/pediatric cancer?
Cancer in children or pediatric cancer is relatively uncommon. Less than 13,500 cases and about 1,500 deaths are reported among kids aged between 0 to 14 years. While more than 1.4 million cases and 575,000 deaths are noted in adults annually. In spite of rare cases, cancer among children remains the 2nd most leading cause of death.
Cancer types that also occur in adults are:
- Leukemia (33%)
- Brain Tumors (25%)
- Lymphomas (8%)
- Bone Cancer like Osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma (4%)
Most common cancers include:
- Neuroblastoma (7% cases)
- Wilms Tumor (5% cases)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma (3 to 4% cases)
- Retinoblastoma (3% cases)
How’s cancer in children different compared to adults?
Cancer in children and adults starts when the cell starts to grow out of control and fails to die naturally. These cells further spread to the rest of the body and cause cancer in different areas. The root cause for cancer in both adults and children is the same, but there’s a difference in the type of cancer caused in children and its treatment procedure.
Types of it are different comparatively
Cancer types in adults differ from the cancers that develop in children. Most cancers develop in adults due to their unhealthy lifestyle and environmental risk which doesn’t happen with children. Only a small number of cancers in children develop due to gene mutation, passed from their parents.
Treatment is most likely to be successful
Most cancers in children respond successfully to certain treatments. It’s a result of different cancer types or due to intense treatments offered to children. In addition, children are free of other health problems than adults that can complicate or worsen with treatment.
Severe long-term complications
There’s an increased risk of side effects on children’s bodies after some types of treatment. For instance, young kids are under a high risk of radiation therapy, and long-term side effects as they are growing.
What are the risk factors and causes of pediatric cancer?
Here are some of the most common risk factors and causes of cancer in children –
Lifestyle and environmental factors
Unlike adults, lifestyle risk factors like smoking, obesity, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol consumption, and unhealthy eating habits can increase the chances of cancer. It doesn’t apply to children. However, lifestyle factors can take a few years to increase the risk of cancer.
Environmental factors, such as radiation exposure is more lily to increase the risk of cancer in children. Studies also suggest that coming under second-hand exposure to smoking (parental exposure) also increases the children’s risk of developing cancer. Though, there aren’t enough cases that develop from detrimental environmental factors.
Gene Mutation
With extensive studies in gene behavior, scientists have understood the reason behind some changes in the DNA inside our cells that causes it to turn cancerous. DNA is the chemical that makes up our genes and orders the cells on how to function. DNA formation also makes us look similar to our parents. DNA also influences the risk of developing a few diseases, including cancer.
Genes control how our cells grow, reproduce and die. Those genes that help in cell growth division, and keeping them alive are known as oncogenes. While Tumor suppressor genes help to slow down cell division, repair error in cell’s DNA, and cause them to die at the right time. Cancer takes place when the DNA changes by turning on the oncogenes or turning off tumor suppressor genes.
Inherited or acquired gene changes
DNA changes can be inherited from the parents that increase the risk of developing cancer. Gene mutations are present in every cell of children’s body and can be tested through blood tests or other body cells. Any type of DNA change is somewhat linked with the risk of cancer, while others can also cause other health and development issues in children.
Inherited DNA changes aren’t the only cause of pediatric cancer, it can be also acquired in the early stages of the child’s life. Gene changes can develop at infancy or even before birth. When cells divide into two new cells, the DNA is copied to offer the same characteristics. Many times, the cell division doesn’t go correct, and errors take place when the cells are growing rapidly. This kind of gene mutation occurs naturally and at any time of life, known as acquired mutation. Acquired mutation takes place in only individual cancer cells, and will not be inherited by their children.
At certain times, cancer-causing gene changes in adults can be identified, in cause such as cancer-causing chemicals in cigarette smoke. But the cause of DNA changes is still not discovered in pediatric cancer. Some causes like radiation exposure and other types show their causes, but there are still to be discovered.
How to prevent ?
In children, lifestyle changes and other risk factors like smoking don’t play as a significant risk factor, resulting in cancer. Some of the environmental factors like radiation exposure are somewhat associated with increasing the risk of pediatric cancer. In cases of mandatory exposure to radiation is simply required, for instance, to treat a child’s cancer through radiation therapy.
In conclusion, there’s very little chance of preventing cancer in children.
It’s extremely rare to inherit a gene mutation that increases the risk of a certain type of cancer. In those cases, doctors recommend preventive surgery to remove an organ to stop the chances of cancer development in that particular area. But again, this is very infrequent.
How to diagnose ?
Here are some of the well-known measures to detect growing cancer in children.
Screening
Going for regular testing or screen in spite of any visible symptoms or not helps to catch an early disease like cancer. Since childhood cancer is very rare, there aren’t enough screening tests available for children to catch cancer, if there are no chances of increased risk.
Inherited gene mutations from parents increase the chance of developing certain kinds of cancer in children. So those kids must be put under careful consideration, and visit regular medical check-ups to become aware of early signs and symptoms.
Symptoms
Cancer in children is mostly recognized in the early stages, either by the kids’ doctor or by the family members. Identifying any signs or symptoms of growing cancer in children is extremely difficult. On top of that, children are most likely to get sick or develop bumps or bruises that conceal the early signs of cancer.
Cancer in children is extremely rare, in spite of that, we must take kids to routine checkups and screen if any unusual signs and symptoms are found. Here are some unusual symptoms found in childhood cancer:
- Lump or swelling
- Tiredness or inactivity
- Easy bleeding or clot development
- Limping
- Continuing body pain or aching
- Recurring headache or vomiting
- Fever or illness for too long, without any cause
- Sudden development of eye and vision problems
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms are also common among other illnesses such as injury and infection. Still, you must take these signs into consideration and see a doctor know the exact cause.
What’s the treatment for cancer in children?
Pediatric cancer treatment involves the type and stage of cancer. Here is the major type of childhood cancer treatment:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Some type of cancer treatment also has to go with high-dose of chemotherapy, followed by a stem cell transplant. Targeted therapy drugs and immunotherapy, are the new option in cancer treatment in children that are becoming effective in treating some type of cancer.
What is Palliative care?
Palliative cancer helps to resolve symptoms caused by cancer and restore the healthy life of the patient and their families. Cancer in children is never easy to undergo, in the family, there are a growing concern and sensitivity attached to the child. In most cases, cancer in children isn’t cured but the suffering could be resolved.
In such a condition, pediatric palliative care helps greatly with taking comprehensive care, starting from the diagnosis to the treatment. These care programs help with various communities and can be operated at home. It helps families with psychosocial support and pain relief.
FAQS on cancer in children/cancer in children/pediatric cancer
What is the most deadly childhood cancer?
Brain cancer affects severely out of cancers in children. More than 500 children are diagnosed with brain tumors annually, leading to 34% of death.
What are the chances of my child getting cancer?
The chances of cancer in children can’t be determined, though cancer is the second most cause of death in children.
What were your child’s first symptoms of leukemia?
The most common symptoms of leukemia are:
- Bruising and bleeding
- Trouble while breathing
- Swelling
- Stomach problems
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained infection
- Anemia
- Bone and joint pain
What causes childhood cancer?
The real cause of cancer in children is still unknown. However, environmental factors and inheritance play a big role.
What is the survival rate of childhood cancer?
Survival rates are determined based on cancer types and various other factors. The survival rate of pediatric cancer has increased, about 84% of children survive for 5 years and more.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
To understand cancer start, growth, and spread, we’ve got to study the smallest constituent first of the body – the cell. We constitute up to trillions of cells formed together into tissue and organs. The cells divide, work, grow, and die from the instruction of the genes present inside the nucleus of each cell. If our cells continue to follow the timely routine of division, growth, and death then we continue to stay healthy.
If there’s any change or damage done to the DNA, our genes can mutate. The damaged genes don’t function properly as the instruction from their DNA is all mismatched. That leads to abnormal changes in the cell, causing the cells to divide and grow out of control that can lead to cancer. Though our immune system handles abnormal smell growth in the body, once cell DNA is damaged, it rapidly reproduces and spreads all over the body. The cancerous cells don’t die when it’s the right time, and continue to grow and divide, forming tumors. Their out-of-control rise affects the surrounding tissues causing complete havoc in the body.
How does cancer start?
When there’s a proper gene development, our cells are instructed to grow and divide timely. We get the same companies of cells when cells tend to divide. There are 2 identical cells from one cell, then those 2 cells divide into 4, and so on. For cells to normally grow and device into more cells takes place when the body requires them, to replace damaged or replace aging cells.
Cancer cells are however different. These cells have gene mutations that turn the normal cell into cancerous cells. The gene mutation in the cells can be inherited, developed over time as we turn old, or happens when you come in contact with things that are capable of damaging the genes like cigarette smoke, the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation, or alcohol consumption.
Cancerous cells are indifferent to normal cells in terms of growth and division. These cells start to grow and divide abnormally, without any control instead of dying and growing to replace those. These cells also remain immature as they don’t tend to mature as much as normal cells. The most primary reason for cancer is mostly due to cells out of control and inadequate growth and vision. Cancer can take place in any cell of the body.
How does cancer enlarge/grow in the body?
Due to gene mutations in cancer cells, the cells don’t tend to grow normally as they should rather they grow out of control and don’t die at the right time. Which causes unwanted cells to grow all over the body. Normal cells grow sufficiently and die when they mature while cancer cells continue to grow despite enough cells present.
Here’s how cancer cells differ from normal cells:
- Uncontrollable growth
- Immature cells, don’t turn mature with specific functions
- Steer clear of the Immune system
- Spread rapidly to other body parts through blood or lymphatic system rather than sticking together.
- Mature into damaged tissue and organs
- Disregard any signs of putting a stop to active vision or dying at the right stage
The wild growth of cancerous cells forms into a tumor. Similar to normal cells, cancer cells also share the same needs. A regular blood supply brings oxygen and nutrients that help the cells to grow and survive. In the case of a tumor, when it’s very small, it tends to grow easily and soaks oxygen and nutrients from the surrounding blood vessels. But when the tumor turns big, it requires oxygen and other nutrients for the cancer cells in abundance.
In need of more oxygen, the cancer cells indicate a tumor to create new blood vessels. The process is known as angiogenesis and it is a significant reason why the tumor grows and expands all over the body. It also creates a tract for the cancer cells to get into the blood and spread effortlessly to the rest of the body. Studies and ongoing research help to cease the growth of blood vessels using drugs and other medication, called angiogenesis inhibitors, prompting the tumor to stop growing or possibly shrink.
How cancer spreads?
As the tumor grows bigger, the cancerous cells takeover the surrounding tissues and structures by forcing a normal tissue beside the tumor. These cells also produce enzymes that collapse the normals cells and tissues from growth. When cancer affects the nearby or surrounding tissue, it’s known as local invasion or invasive cancer.
Cancer can also travel to the rest of the body from one single spot. It is called metastasis. It happens when the cancer cells detach themselves from the tumor and travel to new areas of the body through the blood and lymphatic system.
Does cancer have any specific area of spread? Yes, most cancers tend to spread to a certain location of the body. Which proves quite helpful to medical practitioners to work out the staging system. Different stages in cancer suggest the spread of cancer from where it started to where it is at presently. Most cancers categories the staging system into 1 to 4 stages, known and written in the Roman numerals I, II, III, and IV.
Understanding how and where cancer spreads helps the doctor examine where it grows further. Ultimately, helping them to plan a full-proof treatment and offer proper support to the patient. Though cancer can originate at any location of the body, it is most likely to spread to the bones, lymph nodes, brain, liver, or lungs.
How to understand the cancer stages?
As mentioned earlier, cancers are classified into different stages based on the size of the tumor and how far it has made into the body. Once you identify the stage of cancer, it helps to break down the suitable treatment for the patient.
However, there’s a different staging process known for certain types of cancer than the I, II, III, and IV type. Here are the basic stages are known in cancer:
- Stage 0 or CIS: It’s the very begging of cancer, where you’ve had discovered the abnormal cells that are static, haven’t spread into the nearby area. Known as the pre-cancer stage.
- Stage I, II, & III: At these times, a cancer diagnosis has been proved. The number in the stages decides the size of the primary tumor and how far it has moved.
- Stage IV: Cancer has metastasized (spread of cancer cells to new sites of the body, mostly through the lymph system or bloodstream).
In situ – Translated into “on-site”
In situ stage tells that the cancer is confined to its original site and hasn’t yet invaded the surrounding tissue or spread elsewhere.
- Localized: The cancer cells haven’t escaped to other space beyond their origin.
- Regional: The cells have spread to the nearby lymph nodes, tissue, or organs.
- Distant: The cancer cells have targeted the far-off organs or tissues.
- Unknown: No information found to determine the stage of cancer.
Or
Now, the more advanced staging system of TNM is used to articulate the cancer stage. Here’s what your pathology report contains key letters denoting the following message:
T – Primary Tumor size
- TX: The size of the tumor can’t be measured
- T0: The size of the tumor fails to be located
- T1, T2, T3, T4: Predicts the size of the tumor and how far it has spread
N – Count of regional lymph nodes affected by cancer
- NX – Cancer in the lymph nodes can’t be calculated
- N0 – No cancer spotted in the nearby lymph nodes
- N1, N2, N3 – Outline the number and location of lymph nodes under cancer growth
M – If cancer has metastasized or not
- MX -Fails to be measured
- M0 – Cancer hasn’t spread to the rest of the body
- M1 – Cancer has actively spread all over
Your report would be written by the observation noticed in your body using the above letters. It is more detailed and informative about the cancer growth that helps with seeking timely treatment and care.
What causes cancer to return?
Cancer is also likely to make a comeback, even long after it’s gone. This phase is known as recurrence. Even if a single cancer cell survives in the body post-treatment, the cells proceed to grow and divide rapidly and form a new tumor once again. Cancer can begin at the spot it initially started or spread through the blood or lymphatic system to the rest of the body, forming a new tumor around.
For this reason, doctors perform another treatment right after the first one to ensure complete eradication of cancer, by giving chemotherapy after surgery. It is known as adjuvant therapy. It focuses on treating cancer thoroughly to avoid the risk of it returning. In a few cases, the provided treatment stops working or shows it affects the cancer cells to become more active.
Now, the cancer cells that were on the verge of disappearing or shrinking begin to grow and spread, rapidly. It happens when the genes present in the cancer cells mutate. Treatments like chemotherapy work no longer on mutated genes of cancer cells. If you are unaffected by cancer treatment, your doctor would recommend another treatment that’ll suit your case.
Conclusion
The cycle of cancer starts, growth and spread to the body is extremely rapid. By classifying itself into different stages, doctors can identify cancer development in the body, thereby coming up with befitting treatment. If you notice any early changes in your body, it is highly recommended to get an instant check-up or consult a doctor.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Which is worse, cancer or chemo? Cancer in itself is a life-altering disease but despite the danger of this disease, its treatment is considered much worse. Is chemotherapy tougher than cancer? Although the treatment is always a better choice than none increasing evidence shows up about chemotherapy not being the right choice. What makes chemotherapy not an ideal choice of treatment anymore, is it unbearable? Let’s find out.
Understanding chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is one vital treatment procedure for many types of cancer around the world. It includes the use of drugs to kill cancerous cells. It is useful in stopping the growth, division, and reproduction of cancer cells in the body. Just like other cancer treatments, chemotherapy also has significant side effects that are difficult to deal with for most people. Side effects of chemotherapy vary from person to person.
Cause of chemotherapy side effects
The drugs of chemotherapy are used on active cells. Active cells are cells that are continuously growing and dividing at the same time. When cancer affects the cell, the cells become more active and reproduce rapidly. The cells are from all parts of the body including your blood, mouth, hair follicles, and digestive system. Chemotherapy drugs are used to destroy the fast-growing cells but these drugs travel throughout the body and also damages the healthy, normal cells that grow fast, too. When healthy cells are affected, it leads to a growing number of side effects in the body.
Treatment of Chemotherapy side effects
We can successfully treat and overcome the side effects of chemotherapy. With a medical professional, you can prevent side effects. Nowadays, medications are available of all different kinds to effectively cure the situation. Getting rid of chemotherapy complications is called palliative care or supportive care that is a substantial part of cancer treatment. With the ongoing research and advancement in medical science, scientists are constantly working on developing drugs and treatment ways with fewer complications. Only certain types of chemotherapy cause a greater number of side effects while many other types of chemotherapy side effects are easier to tolerate.
Chemotherapy Side effects
All drugs have their type of side effects. Chemotherapy also involves different side effects varying from person to person. Your side effects can be different from the other place, we’ve mentioned the most common types of chemotherapy side effects. Consult your doctor immediately if you ever experience side effects.
Physical Pain
Chemotherapy causes a handful of physical problems for a short period. It includes:
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Stomach pain
- Nerve-related pain, like burning, shooting pains, numbness, mostly in fingers and toes.
Body pain such as muscle, stomach, or headache fades away after a while but nerve damage worsens with every dose. It turns so extreme that the drug responsible for nerve damage is put to stop use. It can take months, even years for nerve damage to come to end, in a few cases, it never goes away.
To treat the side effects, treatments differ based on the problem that is causing it. It’s vital to discuss the pain with your oncologist while you are taking chemotherapy. Sometimes, the problem can arise from cancer itself, not the treatment side effects. If the pain is associated with chemotherapy, the doctor would give pain-killing medication, regulate chemotherapy doses or block pain signals from the nerves to the brains with nerve blocks or spinal treatment.
Tiredness/Exhaustion
Your body tunes extremely tired or exhausted most of the time. It’s one of the most common side effects of chemotherapy. From experiencing muscle pain to feeling worn out easily, fatigue causes a lack of concentration and challenges to perform daily tasks. Tiredness is a recurring event even after treatment and lasts about three to four weeks but can go on to two to three months, too.
Diarrhea
Loose and watery bowel movements are also an adverse effect of chemotherapy in certain cases. Treating diarrhea at its initial stages can help you from getting dehydrated and also prevent other health problems.
Constipation
Constipation is also a part of chemotherapy. Lack of optimal bowel movement or difficulty in bowel movement leads to constipation. Use of pain medications or other medicines can also constipate. You can prevent or get rid of constipation by keeping yourself hydrated (drink enough fluids), eat a balanced meal, and do some exercise.
Mouth and throat sores
Cells present inside the mouth and throat are also affected by chemotherapy. It develops into hurtful sores in the mouth and throat area, a condition called mucositis. It stays for about 5 to 14 days after the treatment completion. The sores can get infected so don’t share food or come in constant with your family, friends, or children. You can prevent these sores by eating a healthy diet and keeping your mouth and teeth clean. It doesn’t last long, only for a few days, and goes away permanently.
Nausea and Vomiting
Throwing up and feeling sick to your stomach is a common occurrence in chemotherapy. Such side effects depend mostly on the usage of certain drugs and doses. Intake of dose before and after chemotherapy helps put a stop to nausea and vomiting.
Nervous system
Certain drugs used in chemotherapy can also aim nerve damage. The following symptoms in nerve or muscle indicate damage occurred:
- Burning
- Tingling
- Clumsiness
- Out of balance
- Trembling or shaking
- Stiffness in the neck or headache
- Numbness or weakness in hands, feet or both
- Sore, weak, achy, or tired muscle
- Difficulty in seeing, walking, or hearing
With a lower chemotherapy dose, these symptoms can ease and fade out. However, damage can sometimes be permanent.
Hair loss
Losing hair all over the body is a common part of chemotherapy. Starting from little amounts or in larger chumps, the hair starts to fall out of the scalp. It takes in the first few weeks of chemotherapy and increases rapidly into 1 to 2 months of treatment. Usage of certain drugs and doses cause the risk of hair loss so a decrease in its use can cause hair regrowth.
Heart health
Certain chemotherapy side effects travel to your heart. It’s always recommended to check the heart before starting the treatment. If there is an existing heart problem, then the treatment can cause additional problems. Echocardiogram, a common test that used ultrasound waves to create a moving picture of the heart.
Long-term side effects
Many side effects improve with time. However, some complications also return or develop after a while. For example, chemotherapy is prone to cause permanent damage to the heart, kidneys, liver, lung, or reproductive system. While others face cognitive problems, such as difficulty in thinking, focusing, and memory loss for months or years after the treatment.
Late nervous system changes
Many times, kids don’t experience or develop side effects in the month of the year after treatment but these side effects reoccur. Known as late effects, cancer is also likely to return later in life in cancer survivors.
Blood disorders
Chemotherapy affects the bone marrow, responsible for making new blood cells in the body. It is characterized as a spongy tissue inside the bones. Chemotherapy causes a shortage of blood cells. Though the blood cell number returns to normal once the treatment stops, the complication caused by fewer blood cells creates a lot of problems in the meantime.
To check any blood disorder, here are the following test done by doctors:
Complete blood count (CBC): This test helps to identify the levels of the red blood cells and white blood cells in the blood. You can develop anemia if your body doesn’t have enough red blood cells. Its symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness. While a shortage of white blood cells leads to a condition called leukopenia. That increases the risk of developing infections, especially severe ones. Use antibodies immediately if you notice any signs of this condition.
Platelet count
This test includes measuring the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are very vital for the body as it helps the body against excessive bleeding. By plugging damaged blood vessels and forming clots, platelets are effective in sealing any cut. Shortage of platelets causes a condition called thrombocytopenia that involves excessive bleeding and bruising than normal.
Low blood counts are a risk but can be prevented by adjusting doses of chemotherapy. Medications are also available for treating blood disorders that help to increase the blood cell count in the bone marrow. Thereby preventing leukopenia or anemia in people resolving any type of higher risk.
Cognitive changes
Chemotherapy also causes cognitive problems such as trouble in focusing or concentrating on things. This phase is known as chemo brain that doesn’t work normally, scientifically known as cognitive changes or cognitive dysfunction.
Loss of appetite
You won’t feel hungry as you did usually and would eat less. If appetite loss continues after the treatment then you’d lose a lot of weight and turn weak. Lack of nutrition in these difficult times can cause muscle loss and strength and make it difficult to cope up with daily activity.
Sexual and reproductive changes
Cancer treatment can also impact your fertility. In women, the ability to get pregnant and carry a pregnancy while the men’s ability to make a woman pregnant is reduced. Exhaustion and lack of enthusiasm from cancer treatment also affect the ability to enjoy sexual activity. Consider undergoing a Pap test for women before starting chemotherapy that helps to collect a sample of cells from the cervix. An infant or an unborn baby can also be under harm from chemotherapy. In the first 3 months of pregnancy, when the baby’s organs are still forming, the effects can be seen. So, if you become pregnant amid chemotherapy, use effective birth control to survive the severe side effects.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Our immune system and cancer are correlated and interdependent in times of need. Just like the immune system, other organs work together in our body to maintain its proper functioning and health. The immune system, out of all, is vital for the protection of our body against numerous diseases and foreign bodies like pathogens.
For fighting cancer, our immune system plays a critical role. It is designed in a way to identify native and non-native cells in our body that can cause harm. The system is efficient in protecting from millions of germs and fights viruses and infection. However, the immune system is more than about fighting diseases. Here’s what you need to know about cancer and the immune system.
What is the work of the immune system?
The immune system works as a “defense” to our body, protecting it against illness and infection caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites. When a foreign particle comes in contact with our body, our immune system responds and reacts to it. By restricting it from entering the human body and protecting it from further damage, the immune system is the body’s first line of defense. It is also known as immune response.
The immune system is highly essential to people with cancer. Here are the reasons why:
- Cancer makes the immune system extremely weak
- Cancer treatment may weaken the immune system
- Cancer can be fought with the help of the immune system
How can the immune system help to fight cancer?
Certain cells present in the immune system are likely to identify cancerous cells and kill them immediately before their growth. It’s very rare and still not enough to fight cancer altogether. Some treatments use the immune system to fight cancer. Using the two different parts of the immune system, the fight against cancer can be successful. They are:
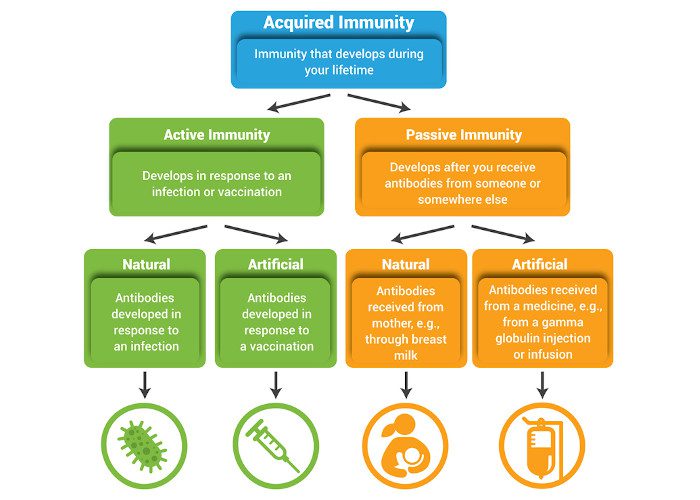
- Inbuilt Immune protection (protection acquired from infancy)
- Acquired Immunity (Protection acquired after a disease)
Inbuilt Immune Protection
Also known as innate immunity, this mechanism always comes into play to defunct the body from harmful damage. Innate immunity reacts immediately to a foreign body and remains always prepared for instant action. Their response involves physical, chemicals, and cellular attack against the pathogens, using natural killer cells, dendritic cells, basophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and neutrophils,
Ways of Inbuilt immune protection
- Forming a barrier by the skin around the body
- Cause stomach acids to kill bacteria
- Inner linings of the guts & lungs produce mucus and trap attacking bacteria
- Hair that moves the mucus and trap bacteria out of the lungs
- Neutrophils, also known as white blood cells to find and kill bacteria
- Urine flow used to flush bacteria out of the urethra and bladder
- Produce useful bacteria in the bowel to prevent other damaging bacteria from taking over.
Book an appointment with Oncology experts at Oncoplus Cancer care.
Complications of Inbuilt Immune protection
Innate protection can be changed with various defects in our body disturbing the shield. Here’s how complications can occur to damage these natural protection mechanisms.
- The wound from surgery or incident or drip in the arms can break the skin barrier
- The use of a catheter into the bladder can create a path for bacteria to reach the bladder and cause infection.
- The use of antacid medicines for heartburn can neutralize the stomach acids that kill good bacteria.
Certain cancer treatments can also cause such complications and disrupt these protection mechanisms. You can temporarily experience a decrease in the number of neutrophils in the body due to chemotherapy. While radiotherapy to the lungs can damage the mucus and hair-producing cells responsible for destroying bacteria.
Neutrophils
It is a type of white blood cell vital for eradicating infection. Neutrophils move to the areas of infection and attach themselves to the attacking bacteria, viruses, or fungi and swallow them up and kill them with chemicals present in their body. Lack of neutrophils in your blood makes you neutropenic.
Cancer treatment like chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted cancer drugs can reduce the number of neutrophils in our blood. Shortage of neutropenic makes you prone to bacterial and fungal infections after cancer treatments.
After cancer treatment, it’s very important to keep these useful points in mind:
- Low neutrophil count causes an infection that can turn severe very quickly
- Experiencing fever or illness could be effective by using antibiotics
- Antibiotic fights severe infection in the body when your blood counts are extremely low.
Bacterial infections after cancer treatment are quite prevalent and spread from one another. So you must avoid interaction with your family, children, and friends after treatment and take precautions to fight them easily.
Acquired Immunity
This type of immune protection is acquired when the body has already fought its battle with other diseases. Our body becomes prepared and can easily recognize each kind of bacteria, fungus, or virus that steps into the body for the very first time. When a certain type of infection harms your body for the first time, the body finds it easy to fight it when it occurs again. Infectious diseases like measles and chickenpox are the perfect example of diseases that occur to us only once as our body fights it effectively the second time.
Vaccinations are used in this type of immunity. The vaccine is composed of a small amount of protein from a disease, not a harmful one. Using it in the body allows the immune system to identify the disease when it enters again and the immune response acts to immediately stop from getting an infection with any disease or viral infection.
Few vaccines include small amounts of live bacteria or viruses in them. These are live attenuated vaccines. Scientists use advanced viruses and bacteria that stimulate the immune system in making antibodies. Infections don’t occur with a live vaccine.
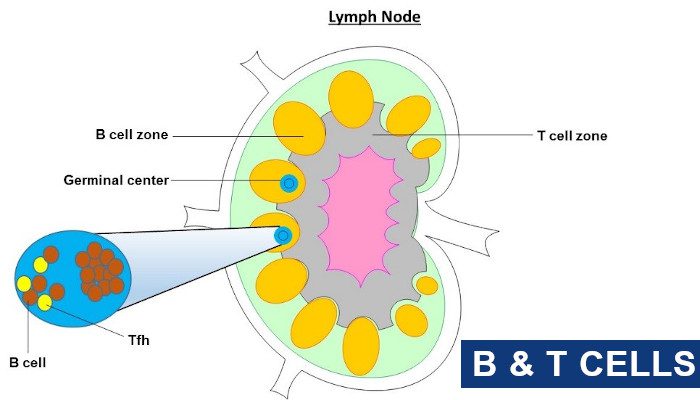
B Cells and T Cells
There are two main types of lymphocytes in the body called B cells and T cells. They are a type of white blood cells involved in the acquired immune response. B and T lymphocytes cells are made from the bone marrow. Similar to other blood cells, these blood cells become completely mature to help the immune system to fight infection and diseases. B cells age in the bone marrow while the T cells mature in the thymus gland. Once they are completely grown, the B and T cells reach the spleen and the mumps nodes to fight infection.
What’s the work of B cells?
B cells produce proteins called antibodies to fight the invading bacteria and viruses in the body. There’s a different antibody produced to fight different types of germs invading the body. The antibodies attach themselves to the harmful bacteria and viruses which marks it as an invader to the body. Marking it helps the body to identify the danger and plans it for killing it. Antibodies are also equipped in finding and killing damaged cells. B cells are a significant part of the immune system. B cells are fast and react quickly by making antibodies against the invading virus or bacteria when it enters the body again.
Antibodies contain two ends. One end attaches the protein to the outside of the white blood cells. While on the other end attaches itself to the germ or damaged cells to catch and destroy it. The ends of the antibody that sticks to the white blood cells always remain the same, known as the constant end. But the other end of the antibody that sticks to the germs differs, depending on the cell type it needs to identify. Also known as the variable end. Each of the B cells creates antibodies with a different end from other B cells. The cancerous cells are complex and differ from normal cells. Hence some antibodies use variable ends to identify cancer cells and attach to them.
What’s the work of T cells?
There are different kinds of T cells, known as helper T cells and killer T cells. The helper T cell is responsible to stimulate the B cells to produce antibodies and help the development of the killer cells. The killer T cells destroy the body’s cells that have been damaged by invading viruses and bacteria, preventing them from further growth and reproducing dangerous cells, and infecting others in the body.
Immunotherapy – How to use the immune system for cancer treatments
Immunotherapy is responsible for treating certain types of cancer. It utilized the immune system to search and kill cancerous cells. Immunotherapy is highly useful in treating cancer as cancer cells as it’s easy to identify cancer cells from normal cells. The immune system is effective in catching and destroying abnormal cells in the body.
Types of Immunotherapy used to treat cancer are the following:
- Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs): Identify and kill certain proteins on the surface of cancer cells
- Cytokines: helps to boost the immune system
- Adoptive Cell Transfer: Change the genes in people’s white blood cells
- Vaccines: Help the immune system to identify and kill cancer
The immune system is potent in keeping our body safe and protected from detrimental viruses, bacteria, and fungi. With changing times and advancements in ongoing technology and research, immune stem can efficiently help in fighting cancer.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Once your cancer treatment ends, going back to our routine makes life more comforting and healing. It distracts and gives back the normal life outlook again once we return to our familiar routines, one such is work. Your workplace can renew your focus and concentration beyond cancer. Deciding to resume back your work is an excellent and powerful move, and if you’ve made up your mind, then you’re going to be alright. However, starting work after cancer requires some precautions, extra care, and planning to ensure you are mentally and physically strong to cope up with the transition.
What does it take to return to work as a cancer survivor?
As someone who’s just survived cancer, going back to work is not an easy decision. Many a time, there’s emotional and mental stress that comes along with cancer treatment that affects your work plans. If you’ve taken the strong decision to return to work, the first and foremost step must involve the doctor’s approval.
You need to make sure to go through the long-term side effects of your treatment, type of job and physical demands of it, and a need for follow-up care. If you’ve passed the doctor’s inquiries, you must reach out to your employer through a virtual or in-person meeting to discuss the details of the return. As a cancer survivor, you must discuss medical appointments, unpaid medical leave, work overload, and other difficulties with your employer to inform him where you stand. Once the employer agrees to your new changes in work, you can think of moving ahead.
How can work bring a change?
Returning to work is not going to be difficult if you are mentally prepared and know the benefit that comes along with it. Work is one of the great joys of people’s life that helps to build stronger relationships with others. Here’s to some reason how work will bring a new form of motivation and happiness in your life:
Income: Money is indisputably one of the most essential in life. After paying for the treatment and everything, financial security comes from work. There would be post-cancer medication and needs you’ll have where money can help upon, even help with your lifestyle thereby boosting your self-esteem.
Daily Practice: Work is a commitment that creates a routine in your life where you’ve always got to show up. Which is your case is quite healthy and beneficial as having a specific timing of work and a fixed break would keep your body active.
A Break: With cancer comes a loss of stress related to the financed, family, friends, health, etc which only mitigate your situation. So to take a break from the constant conversation of cancer and associated worries, it’s better to develop a distraction that takes you away. Work proves to be the best option as a distraction as having a fixed task assigned to you regularly will help your focus on those.
Socializing: Go out, have a conversation about other people’s lives and their problems. At the workplace, socialization is great since you meet your colleagues, clients, or vendors around that help you get in touch with the outer world rather than being stuck with oneself. Studies have shown that socializing with others at our lowest point of life improves mental and emotional help and decreased depression signs.
Even with our listed benefits, work can be challenging as a cancer survivor. You won’t just have to tackle physical but also mental distress, and other common hurdles of your workplace. Here are our listed problems you will face and how to brace yourself for them.
Problems that come along with work
You can experience fatigue, loss of memory, irritation, discomfort, and other side effects.
Solution:
Reach out to your medical teams of experts about work and your schedule to see if they’ll advise you with the necessary medication to fight the side effects efficiently.
Be comfortable with your pace. Don’t compare with what you were before and what you are now. You are this powerful person who just battled cancer for months and now your body will take time to heal. Even if your work takes longer nowadays, then allow yourself at that time.
If you get exhausted while working then take immediate breaks. Device your working hours into two or three lots, with some resting time in between to remain active.
Find it difficult to remember dates, timing and details then make remains, schedule work, and create time-tables. Always keep a notepad with you all the time to remind you of your work, important notices, and many more.
Book an appointment with Oncology experts at Oncoplus Cancer care.
Essential Steps to take before starting work
Reach out to Human Resource or employer
Your body and mental state are still vulnerable and need special allowances while working to carry out your responsibilities. Discussing or informing your HR or employer to see if they’d allow these changes with different working hours is a wise decision. You must explain to them what and why you need to create some changes so that they’ll understand your situation.
Though you won’t exactly get what you need however there would be a great help from your colleagues once you explain to them what your body is going through. Since people don’t know and it’s always good to let others know how and what you feel. Many enterprises allow work from home from keeping you safe from infection and other things. Don’t participate in travel-based assignments yet, wait till you feel ready and physically fit.
Don’t be guilty with the new changes & news you
What you’ve gone through, nobody else has which makes you special, powerful, and strong. Never keep that out of your mind so give your body enough time to gradually reach the heights of how you worked earlier. Don’t be guilty of your situation and put yourself down or inferior in front of others. Accept the new you and as time passes, you’ll find the old speed and pace.
Know your rights
Look out for worker allowance, leaves, insurance, etc to discover your option ahead. Your company has a policy on sick leaves, and other rights that you can access when you need them.
Pay attention to health
Even if work starts, don’t forget to make a schedule for food, medications in between breaks to avoid any complications. Skipping out on meals or medicine is not good. Also, don’t forget to keep yourself hydrated at work by sipping water consistently every day. Keep a water bottle in front of you so you are constantly reminded of it.
Apart from food, taking a few hours for resting and relaxing in a day also helps greatly for your body. Don’t get overworked, work at only the workplace while consistently doing relaxation activities such as meditation, light exercises, and deep breathing.
Seek Comfortable environment
Nothing beats comfort, especially at a workplace where you spend quite a lot of your daily life. Check your table and chair if they are suitable or not, if not then get an ergonomic chair for relaxing sitting arrangement. Bring along essential supplies that you might need like a foot-stool, heating pads, neck support, or others.
Look forward to new, positive changes as you’ve already passed the biggest challenge. Now, you are ready to tackle small hurdles and allow yourself to heal with time.
FAQS on returning to work after cancer
Your common question on work after cancer answered.
Q. Do I need to inform my new employer about my cancer?
No! It depends on you. If you want to mention your medical history or ask for medical leaves, follow-up visits, or remaining chemotherapy sessions, you might need to explain it. Other than this, your employer just needs to know if you’re qualified and capable of the job offer.
Q.Why do people treat me differently after surviving cancer?
Cancer can be concerning for everyone. Your colleagues are bound to bring our cancer in the initial stage due to curiosity. If you don’t prefer talking about it, then you just need to politely decline to talk about it with others and they’ll understand. Give some time and both of you will gradually return to normal and you’ll no longer feel sensitive talking over cancer.
Q. Would I be able to work similarly to before?
It’s difficult to say because your body has still not recovered yet. You won’t be able to work to your full potential due to physical tiredness and mental distress. However, you can take extra measures to tackle such situations. Here’s how you can do it.
- Learn to adapt to your new speed
- Keep calm and cope with new changes
- Accept and ask for help during these times
- Go easy with work competition
- Set priorities of task
Q. Can anyone train me for work-life better?
Yes! Before you take the big step, seek help from an occupational therapist to improve on everyday tasks associated with work. The occupation therapist will train and advise you with work citation and tackle specific challenges and restrictions. If you are struggling with physical changes like uncomfortable with prolonged hours of sitting, then physiotherapists can increasingly help decrease pain and build muscle strength. Or experiencing trouble with memory and focusing then neuropsychologists would work on enhancing your memory, confidence, and focus.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
How does tobacco use lead to cancer?
The relationship between tobacco use and cancer goes hand in hand, especially resulting in lung cancer. Consuming tobacco products leads to 9 out of 10 cases of lung cancer and the cases are only increasing every day now. Not just lung cancer, tobacco leads to bladder, cervix, colon & rectum, esophagus, kidney & renal pelvis, lungs, bronchi, trachea, blood, stomach, and liver cancer. The use of tobacco is lethal and its consequences are severely damaging to people’s health. Almost 1 out of 5 cancer deaths happen due to its use.
Most people misunderstand their damage just because there are various forms of tobacco in the market. Some might appear safe and seem without any health impacts but it isn’t simply true. All forms of tobacco are harmful, even the new trend of e-cigarettes.
What are the chemicals present in it?
Tobacco leaves are used in cigarettes, pipe tobacco, and cigars. Additional components are added just for the flavor to cover the unpleasant taste of the smoking experience. About 70 different cancerous chemicals are produced from the smoke of tobacco. These chemicals are known as carcinogens. Whenever you breathe in the emitted smoke environment, the chemicals reach into your bloodstream and spread to all parts of your body.
All these chemicals may harm your DNA, which’s responsible for making new cells, and tells each cell what and how to function. An injured DNA fails to do the job correctly and leads to different cell growth from what happens naturally. Cells either grow inadequately at any part of the body and turn cancerous.
The harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke are nicotine, hydrogen cyanide, lead, ammonia, arsenic, formaldehyde, radioactive elements like Uranium, carbon monoxide, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), benzene, and nitrosamines. Most of these chemicals cause cancer while others result in heart disease, lung cancer, or other serious health problems. All major chemicals are just derived by just burning tobacco leaves themselves, not from additives.
Are there any radioactive materials in tobacco smoke?
Yes, radioactive materials are present in tobacco leaves which are used in making cigarettes and cigars. The tobacco leaves get radioactive materials from fertilizers and soils used for their growth and depending on the among, it can vary in each plant. The radioactive materials are released into the air and reach a person’s body when tobacco is burned by smokers. That is one of the biggest reasons for causing lung cancer in people.
What are other harmful tobacco products?
- Cigar: It’s similar to all other lethal tobacco products with carcinogenic compounds but with different levels of chemicals present in them. Since cigars are much more preferred after aging as it helps to blend their different flavors, there’s a high concentration of nitrogen compounds in them. Using fermented cigar tobacco emits various kinds of tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNAs), some of the major cancer-causing substances out of all. Cigars packaging also makes it more since it is less porous than a cigarette wrapper, there’s incomplete combustion of tobacco. That results in a greater concentration of ammonia, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides – all major lethal cancerous substances.
- Smokeless products: Snuff and chewing tobacco are some of the products of smokeless tobacco that don’t require burning like cigarettes or cigars. Unfortunately, they are equally damaging to our health with various harmful chemicals including a high concentration of TSNAs.Elements like benzo a pyrene and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are some of the influential cancer-causing elements found in smokeless tobaccos. Similar to other tobaccos, they also contain radioactive substances. Smokeless tobacco is consumed through the mouth resulting in various types of cancer. Other alternatives like Snus are more moist snuff consumed without spitting. Used first in Sweden and Norway, it is also available in India. Though it has lower levels of nicotine and TSNAs compared to other smokeless brands, it is still very addictive and causes a few types of cancer.
- E-cigarettes and other devices: We have also witnessed electronic smoking types such as e-cigarettes and other electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) used as a modern alternative to tobacco products. E-cigarette brands claim that these products are safe to use but it’s very unlikely. The aerosols from these electronic smoking devices contain flavorings, addictive nicotine, and various other cancer-causing chemicals that are extremely toxic. It’s more worrisome as a larger group of youngsters fall prey to these new products. Though there’s less amount of harmful chemicals compared to the usual cigarettes, the replacement of nicotine and other substances are lethal to our health. Since it’s a new product in the market, its ingredients are under study to find out its long-term effects.
Book an appointment with Oncology experts at Oncoplus Cancer care.
What are the benefits of quitting?
After looking at the long list of detrimental effects of tobacco smoking, it’s a wise move to quit smoking at any time. It’s never too late, the sooner you take the step forward, the better you’ll feel and stay free of diseases. There are various benefits of quitting smoking, here are some of the most feel-good ones motivating you to take the step now:
- Lower risk of diabetes
- Increased life expectancy
- Boost working of blood vessels
- Food tastes delicious than ever before
- Your taste & smell return backs to normal
- Rarely gets tired or exhausted easily
- Better hygiene and smell
- No more discolouration of teeth and fingernails
Quit smoking now and save yourself from future ailments.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Does plastic use cause cancer?
Plastic, as sinful as it is for our environment, possesses the possibility to be a threat to our body in the form of cancer. In recent years, the use of plastic and its exposure to our health through various products turned out to be notably unsafe. So we need to dig deeper on this issue to resolve such severe concerns since plastic comes in use with every one of our needs. From bowls to water bottles, plastic is accessible at every corner of the utility department.
According to a study, few chemicals in plastic dissolve some plastic into the food and beverages we consume. Those chemicals result in severe health problems like metabolic disorders and decreased fertility. It can get worse if the plastic is exposed to heat as it elevated the damaging chemicals at a faster and increased amount into the items than at a normal state.
Today, we’ll uncover the fact if plastic use can lead to cancer. And if we can do anything to reduce the negative outcomes caused by our health.
What is plastic made of?
Primarily, we must know our subject before claiming it hazardous. Plastics are more complex than we often assume. Plastics care not just one thing, they are of many different kinds and possess their different names based on their composition. For example, polypropylene, polyethylene, polyethylene, polycarbonate, and terephthalate. All of them contain a variety of chemicals with different properties like antioxidants, plasticizers, and colorants.
In general, plastic use and exposure have caused severe damage to people. What’s important to note here is many plastic containers publicly state that their product contains chemicals but in small amounts indicating there’s no chance to worry. But if we continue to use the product repeatedly for various days, months, and years, the effects would lead us to various health hazards. The initial amount of the product might look small but continued use only helps to add more each day.
Along with chemical exposure, plastic products put pregnant women at a greater risk. The harmful chemical release reached the exposed fetus in the womb that affects them severely. Out of the most known detrimental chemicals are phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA). The two chemicals are called endocrine disruptors and are known for interfering with the hormonal system in our body.
Here’s how both these plastic’s chemical impact our body
Phthalates
Phthalates are a group of chemicals used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to make plastic more flexible, plant, and hard to break. After consuming them via food items, these chemicals work as male reproductive toxicants. It also affects women. These chemicals are prominent for making vinyl plastics soft and flexible, used in multiple product manufacturing. We are under the highest exposure of these chemicals since it is present in toys to medical devices. Adult women, especially, are under higher threat compared to men since phthalates used in various cosmetics like shampoo, soaps, and body washes.
Bisphenol A
BPA comes under the use of making hard types of plastic called polycarbonate often used in making containers for storing food and beverages, such as water bottles, lunch boxes, and storage cans. Recently, Bisphenol A is getting a lot of attention due to its adverse health effects in humans and rodents. The chemical is lately in controversy for its possible impacts on the brain and prostate glands of fetuses, infants, and kids. In 2011, a study proved the presence of high levels of BPA in pregnant women and their infants would be more likely to exhibit anxiety, hyperactivity, and depression.
These two chemicals are in attention due to their growing negative impacts on health, there are many other chemicals in plastics with similar impacts including antioxidants, and colorants.
Do microwave plastics worsen our health?
Heating plastic is always a disadvantage to health than eating out them at natural temperature. So depending on different plastic forms, heating them in a microwave can rigorously release harmful chemicals in the food and beverages stored in it. Foods rich in fat are particularly more likely to increase the release of chemicals.
Many plastics claim to be microwave-safe by the FDA. Getting FDA’s approval for claiming your product requires manufacturers to test the container, evaluate the container timing in the microwave, how much anyone is likely to eat out of the container and estimated the temperature of the food inside it. If the amount of chemical released from the container into the food is lower than a maximum allowable amount set, the product is free to be called microwave-safe. But ultimately, the product is never fit or free of chemicals.
Hence even after being aware of the plastic type and additives used, the safety advice would be to avoid the use of heating food in plastic.
Are regular plastics non-toxic for use?
Microwaves elevate the chemical release in the food items from plastic, not the only way the food gets contaminated by chemicals from plastics. Food and beverages stored in plastic containers, even without microwaves release chemicals in the food items. Plastic’s abundant chemical release gets altered if kept in a heating environment or under the sunlight. Tomatoes and other acidic food easily absorb chemicals from the lining of the food cans. Apart from food containers, chemicals containing home decor things containing phthalates, release gases in the air over time, increasing the chances of inhaling the harmful chemicals. Even plastic vapors can release chemicals in the food, even if the plastics are not in contact with it. Vapourized plastic containers release their gases into the food item when used as a plastic splatter lid over a bowl in the microwave.
Book an appointment with Oncology experts at Oncoplus Cancer care.
Are plastics free of phthalates and BPA considered safe?
It’s difficult to say if other types of plastics, if not phthalates and BPA, are safe. Companies who claim to have eliminated the problematic chemical from its product ingredient, its replacement is just another chemical which we don’t know much about. It can or is almost equally toxic.
It’s a common tactic used by companies to replace a controversial chemical with a new one. The new chemical has no evidence supporting its benefit or risk-free features so it’s never a safer option. Usually, companies switch BPA with a different chemical called bisphenol S or BPS. Earlier, there was less information available on the internet about its state of use but recently, it turned to be detrimental as well.
In 2011, the Environmental Health Perspective published a study testing commercial plastic products that claimed to be BPA-free. The result proved that almost all of them released chemicals with estrogenic activity. Some of them even had more estrogenic activity than BPA.
Book an appointment with the best kidney cancer doctors in Delhi for Kidney Cancer Treatment
Steps to protect yourself
Avoiding plastic use at all costs seems impossible due to every product found made in plastic. Limiting plastic use as much as possible, especially when a woman is pregnant and along with food items can help greatly.
How to limit the use of plastics:
- Replace your plastic water bottles with your steel, glass, or ceramic water bottle.
- Decrease the amount of canned food you consume and your child used daily.
- Go with children bottles with labels that are free of BPA.
- Don’t recycle carbonless receipts at cash register receipts as receipts with BPA can spread the BPA onto other problems made with recycled products like napkins and toilet paper.
- Use plastics with the number 7 recycling symbol on the bottom. Don’t stick to plastic without a label saying “PLA” or a leaf symbol on it as it may contain BPA.
How to limit chemical exposure from plastics?
Stop cooking food in plastic containers or use them in roasting or steaming: As discussed earlier, plastic under heat is prone to realize higher amounts of chemicals into food than at regular temperature. Limit the use of microwaves or even if you do, use a glass container to heat or bake anything.
Switch to glass, enamel-covered metal, stainless steel pots, pans, porcelain, and containers for storing food and beverages or even when the food item is hot.
Lookout for Plastics with recycling symbols of 2, 4, and 5 to use: Plastics label with recycling symbol 7 and along with a leaf symbol is good to go.
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.