Sometimes, if you find that there is a rash on your breast or that your breast is swollen, it is possible that you are suffering from a breast infection. But, in some cases, it is a sign of an inflammatory breast cancer that grows in your body over weeks or months. This is a rare form of cancer, but it is a fast-growing cancer that requires immediate treatment. A breast infection, also known as mastitis, is a condition that occurs when the breast tissue becomes infected. It usually occurs in women who are breastfeeding, but it can also occur in women who are not breastfeeding. The symptoms of IBC are swelling, pain, redness, and enlargement of the breast. In Delhi, the best breast cancer treatment is available at Oncoplus Hospital. In this blog, you will read about whether your rash is caused by a breast infection or inflammatory breast cancer.
Read More: 6 Lifestyle Changes To Improve Life After Breast Cancer Treatment
Symptoms of Inflammatory Breast Cancer:
The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer are as follows:
- Pain, itchiness, or tenderness in the breast.
- Redness and swelling in the breast
- Warmth or heaviness in the breast.
- Thickening or a lump in the breast.
- Nipple discharge that may contain pus
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever and chills.
- If the breast nipple goes flat or inward,
- If the patient finds a swollen lymph node under the arm or near the collarbone,
The symptoms of IBC can develop quickly, within days or weeks. If you have persistent symptoms, then it is important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. A doctor may perform a physical exam, imaging tests, and a biopsy to confirm whether the symptoms are due to a breast infection or IBC.
Read More: Common Misconceptions About Breast Cancer
Factors That Cause Inflammatory Breast Cancer:
There are several factors that are known to increase the risk of developing inflammatory breast cancer. They are as follows:
- Age:
The primary risk factor for IBC is age. Women over the age of 50 are more likely to develop breast cancer than younger women.
- Gender:
This type of cancer is more likely to occur in women, but it can affect people of all genders.
- Family History:
Family history is another factor that can increase the risk of developing IBC. The women whose relative has had breast cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
- Other factors:
Other factors that can increase the risk of IBC include obesity, exposure to radiation, alcohol consumption, and hormonal factors. Women who have had previous breast biopsies or have dense breast tissue may also be at a higher risk of developing IBC.
Diagnosis of Inflammatory Breast Cancer:
There are several diagnostic tools and tests that healthcare providers use to diagnose IBC. Some of the common diagnostic tools are as follows:
- Physical examination:
A healthcare provider will perform a thorough physical examination of the breast, in order to look for signs of redness, swelling, or other changes.
- Imaging tests:
Imaging tests such as mammography, ultrasound, or MRI can help identify any suspicious areas in the breast. Generally, IBC and breast infections appear similar on imaging tests.
- Biopsy:
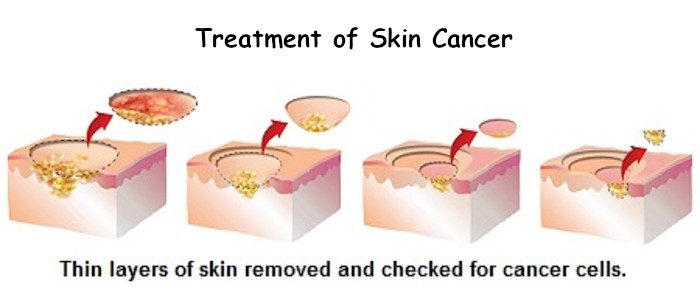
During a biopsy, doctors remove a small sample of breast tissue for examination under a microscope, which is the only way to diagnose IBC. Typically, if IBC is suspected to have spread to nearby lymph nodes, doctors may recommend a biopsy of the lymph nodes to determine the extent of cancer spread.
Treatment for Inflammatory Breast Cancer:
The treatment for IBC usually involves a combination of chemotherapy (which uses drugs to kill cancer cells), surgery (removes the entire affected breast), and radiation therapy (which uses radiation to destroy cancer cells). It is important to start the treatment as soon as possible to prevent the cancer from spreading in the patient’s body.
In conclusion, a rash on the breast can be a sign of a breast infection or inflammatory breast cancer. While the symptoms of a breast infection and IBC can be similar, it is important to visit a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. If you have persistent symptoms, such as a red, swollen breast or persistent itching, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. With early detection and treatment, both breast infections and IBC can be successfully treated at the best cancer specialist hospital in Delhi. Oncoplus Hospital is famous for providing the best cancer treatment to cancer patients.
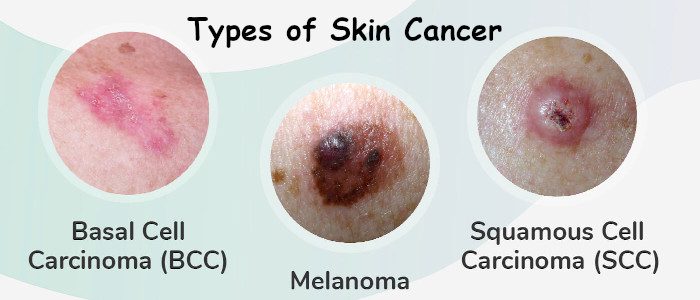
Tips for Preventing and detecting skin cancer
As the days grow hotter and sunny, outdoor activities such as running, biking, swimming does not stop. These activities are necessary for our lives as working outdoors is good for physical and mental health, and spending time in the sun also assists the body to get the sunshine vitamin D.
Exposure to UV radiation from the sun can be very harmful for the skin, and can damage the DNA in skin cells, making mutations, which can cause skin cancer. Studies state, five or more sunburns can double the risk of melanoma.
Preventing and detecting skin cancer while enjoying the outdoors becomes very important. Protect yourself from harmful UV rays or artificial sources of radiation such as tanning beds. Experts suggest to avoid the sun between 10 am – 4 pm as the UV intensity is highest. Using sunscreen and protective clothing is extremely necessary; avoiding tanning beds at all costs.
There are two types of risks associated with skin cancer. There are risks, which we can control, and there are risks, which we can do nothing about. Exposure to ultraviolet light is a modifiable risk factor for the development of skin cancer. Experts suggest to use sunscreen, apply liberal amounts of sunscreen at least every two hours when you are outside, and more often if participating in water activities. On a hot sunny day, if applied liberally one could use up to an entire bottle of sunscreen.
Other way of blocking the harmful UV rays is by wearing protective clothing, which have an ultra violet protection factor, where one doesn’t have to worry about reapplication of sunscreen if you are wearing the UPF clothing. Do add sunglasses and wide hat
Fields recommends adding a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses to other UPF clothing for best protection. This helps protect the head, ears and eyes from UV while spending time outdoors.
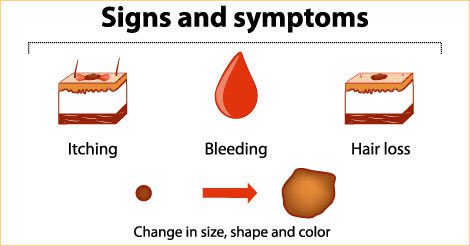
Do not wait. Even a tiny spot on the skin could be a sign of melanoma or other kinds of skin cancer. Do not neglect the sign, and consult with Skin Cancer specialists at Oncoplus Hospitals, Defence Colony, New Delhi, India. Make prevention a part of your routine as it is never too late to start good habits to protect yourself for UV rays.
Always Wear sunscreen and/or protective clothing, seek shade when possible, to reduce UV exposure, avoid tanning beds and always self-examine your skin for new or changing spots. Give yourself a self-examination, looking for any new or changing spots on your skin. Early detection and treatment is key to successfully remove skin cancer. Some of the deadliest forms of skin cancer, can spread, if left untreated.