Cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the kidney cells. The kidneys are the two bean-shaped organs located behind your abdominal organ on either side of the spine. It plays a crucial role in filtering blood and removing waste products from the body. The common type of kidney cancer is the renal cell carcinoma. Other types of kidney cancer include transitional cell carcinoma, Wilms tumor, and renal sarcoma. The major signs of kidney cancer are blood in the urine, abdominal or back pain, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, tiredness, high blood pressure, high calcium, and a lump in the kidney area. Regular checkups with a healthcare provider help you detect kidney cancer early, which improves your chances of a successful treatment. Oncoplus Hospital, the cancer hospital in Delhi, wants to inform you about kidney cancer. In this blog, you will learn the facts about kidney cancer.
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer:
The symptoms of kidney cancer can vary from person to person, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all in the early stages of the disease. The most common symptoms of kidney cancer are blood in the urine, pain in the side or back, weight loss, fatigue, fever, swelling in the legs or ankles, loss of appetite, and tiredness.
Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer:
- The risk factor for kidney cancer is smoking. Cigarette smoke contains numerous chemicals that can damage DNA, and smokers are more likely to develop kidney cancer than non-smokers.
- Other risk factors include obesity, high blood pressure, and exposure to certain chemicals.
- Chronic kidney disease is also a risk factor for kidney cancer, as are certain inherited conditions such as Von Hippel-Lindau disease, hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma, etc.
- If close family members have a kidney disease, then the risk of having kidney cancer increases.
Prevention Tips
While not all risk factors for kidney cancer are preventable, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk. These include quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, managing high blood pressure, and avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals. It is also important to get regular check-ups and discuss your kidney health with your healthcare provider. By taking proactive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing kidney cancer and other kidney-related illnesses.
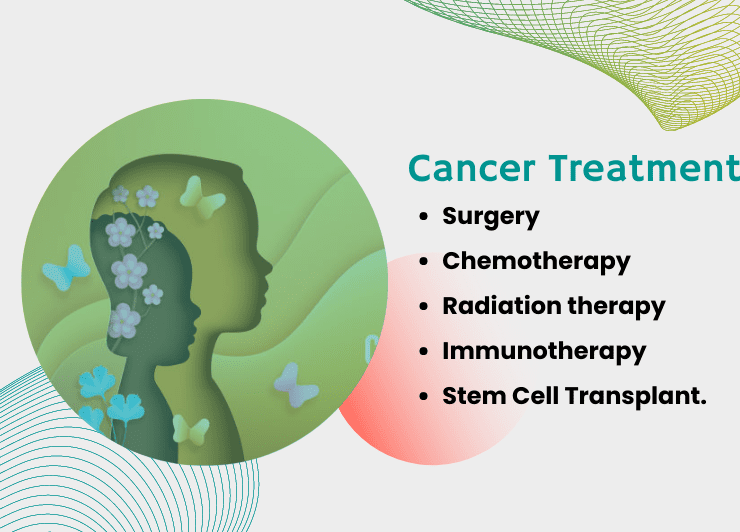
Treatment Options for Kidney Cancer:
The treatment options for kidney cancer depend on several factors, such as the stage and location of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. The treatment options available for kidney cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
- Surgery:
Surgery is basically the primary treatment for kidney cancer. The most common surgical procedure is a radical nephrectomy, which involves removing the entire affected kidney, surrounding tissue, and nearby lymph nodes. In some cases, a partial nephrectomy surgeon removes only the tumor and a small amount of surrounding tissue while preserving the remaining healthy kidney tissue.
- Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses radiation to kill cancer cells. It is not a common treatment for kidney cancer but may be used in some cases, such as when surgery is not an option or when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Read More Blog:- Treatment Of Cancer With Radiation Therapy
- Targeted Therapy:
In targeted therapy treatment, doctors use drugs to target specific molecules that are responsible for the growth and spread of cancer cells. These drugs can block the cancer cells that are used to divide and grow, or they can trigger the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Read More Blog:- Targeted Therapy For Treating Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
- Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment in which doctors use medications to boost the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. The most common type of immunotherapy for kidney cancer is checkpoint inhibitors, which block proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells.
Read More Blog:- How Does Immunotherapy Help In The Fight Against Cancer?
At Oncoplus Hospital, you can consult the best cancer doctors in Delhi. In conclusion, kidney cancer can be treated with a combination of surgical, radiation, and systemic therapies. The choice of treatment depends on the individual patient’s situation and a multidisciplinary team of doctors and specialists.
Treatment of Cancer with Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy is also known as radiotherapy. It is a type of cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells. This therapy is used to treat different types of cancer. A radiation oncologist specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer. Many different forms of cancer can be treated with radiation treatment, which can also be used with chemotherapy or surgery. With the help of this therapy, cancer cells stop growing and are destroyed. There are basically two types of radiation therapy: external beam radiation therapy and internal radiation therapy. In this article, you will learn about how radiation therapy helps treat cancer.
How does radiation therapy help treat cancer?
Cancer develops in the body when healthy cells undergo changes and if there is uncontrolled growth of the cells. The cancer cells grow, divide, and multiply faster than normal cells. Radiation therapy damages the DNA of the cancer cells and stops them from growing and getting destroyed. Radiation therapy affects only the target area of the body, where the cancer cells are located, and not the whole body. During the treatment, some of the healthy cells also get damaged, but they heal when the treatment is completed. This therapy does not immediately kill cancer cells. This treatment takes weeks to kill cancer cells, and the cancer cells keep dying for months after the radiation therapy is completed.
The radiation therapy is given to the cancer patients according to the type of cancer they have or how much it has spread. This radiation therapy can be given along with other different treatments to treat cancer. This therapy depends on many factors, such as the type of cancer, size of the tumor, location of the tumor, closeness of the tumor to the other normal tissues, your medical history, your age, etc.
Types of radiation therapy:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy:
In external-beam radiation therapy, radiation is delivered from a machine outside the body. This machine sends radiation to the target area of the body from different directions. The therapy affects the tumor and avoids the surrounding healthy tissues, which are located nearby. This therapy is given to patients for several weeks. External therapy is of different types, such as:
- Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT)
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
- Proton beam therapy.
- Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT).
- Stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT).
- Internal Radiation Therapy:
Internal radiation therapy is also known as brachytherapy. In this radiation therapy, radioactive materials like seeds, ribbons, or capsules are kept in the cancer cells or the surrounding tissue. This is the permanent implant.
In systemic radiation therapy, this type of radiation therapy can be given through a vein via an IV line or through an injection. After this therapy, your body fluids give off radiation via urine, saliva, and sweat.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
The majority of cancer patients receive radiation therapy over a number of sessions, and they do not get the full dose at once. So, during sessions, your tissues get time to recover, which reduces side effects. However, patients report vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, headaches, skin irritation, hair loss, mouth sores, decreased appetite, and pain in the throat when swallowing.
Radiation therapy helps treat cancer in the body. But like other treatments, this therapy also causes side effects such as skin changes, discomfort, etc. There is a risk of developing a second cancer after undergoing this therapy. In the majority of cases, radiation therapy removes the existing cancer.
How to Cure Childhood Cancer?
With the advancement of technology, about 80% of childhood cancers can be cured globally. In high-income countries, as resources become available, childhood cancer can be cured. But the percentage is low in India because of a lack of awareness. The reasons for lower survival rates in low-income countries are a delay in diagnosis, inaccessible therapy, an inaccurate diagnosis, if the patient leaves treatment in between, and death from side effects.
For kids and teenagers, cancer is the main cause of death. Generally, the most common types of cancer in children are leukemia, lymphomas, brain tumors, and solid tumors. In most cases, screening cannot detect or prevent childhood cancer. By using generic medications and other cancer treatments, like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplant, childhood cancers can be cured. Most importantly, pediatric cancer can be treated in any socioeconomic setting. In this blog, you will learn the method for curing childhood cancer.
The warning signs of cancer in children:
- If there is blindness, a bulging eyeball, a white spot in the child’s eye, a new squint, etc. are some of the few warning signs of cancer.
- In case a lump is found in the abdomen and pelvis, limbs, testes, glands, head, and neck.
- Loss of weight and appetite are seen in children.
- If your child has a high fever, pale skin, fatigue, easy bruising, or excessive bleeding, seek medical attention immediately.
- If there is a change in behavior, balance, headaches, or an enlarging head, consult your doctor.
- Patient is having pain in her bones, joints, and back.
The Causes of Cancer in Children:
Normally, there is no known cause for childhood cancers. Cancer can affect any region of the body and affect people of all ages. It starts when there is a genetic change in the single cells. Then it grows into a tumor and affects other parts of the body. If the treatment is not given, it leads to death.
Adults are more likely to develop cancer if they have an unhealthy diet, such as smoking or eating unhealthy foods. But the children do not have any unhealthy habits that increase their risk of cancer. If the child has a family history of cancer, then it will increase the risk of having cancer.
But childhood cancers are caused by a DNA mutation that is not inherited but occurs randomly. There are very few cancers in children that are caused by lifestyle or environmental factors.
HIV, Epstein-Barr virus, and malaria are some of the chronic diseases that increase the risk of developing childhood cancer. In low-income countries, this is very important. Hence, it is very necessary to get vaccinated, as other infections can increase the risk of cancer.
Effective Cancer Prevention Strategy for Children:
Normally, it is not possible to prevent childhood cancer in children, but it is possible to reduce cancer in children. With early diagnosis, correct treatment, and palliative care, you can cure cancer in children. Early diagnosis of cancer improves the survival rate of many children suffering from cancer. If cancer is identified early, then it will respond to treatment, the patient will suffer less, and the treatment will be less expensive.
If the child gets an early diagnosis, then appropriate therapies are available for the patient, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiotherapy. As all children suffering from cancer cannot be cured, palliative care should be given to those who suffer from cancer.
How Does Immunotherapy Help in the Fight Against Cancer?
Immunotherapy is basically a cancer treatment that uses your own immune system to fight and destroy cancer cells. Because the cancer cells are different from normal cells, they do not die. This therapy uses substances that are made by the body to boost the immune system. It is used to treat many different types of cancer. The specialist uses this therapy alone or sometimes uses chemotherapy to treat cancer patients. In this blog, you will learn how immunotherapy helps fight cancer.
What are the Different Types of Immunotherapy?
The immune system of a person consists of complex processes, i.e., cells, organs, and proteins. In this, cancer cells continue to grow. Immunotherapy helps the immune system to slow down the growth of cancer cells or stop cancer from spreading in other parts of the body. Doctors recommend immunotherapy to the patient according to the type of cancer, location, and size and also on which part of the body the cancer has spread. Treatment also depends upon various factors like age, general health, and body weight.
The Different Types of Immunotherapy:
- Non-specific immunotherapies
Non-specific immunotherapies help your immune system destroy cancer cells. There are different types of non-specific immunotherapies, i.e., cytokines, which are part of the immune system. Interferons are produced by the immune system to alert your body and slow the growth of cancer cells. Interleukins pass messages between cells.
- Monoclonal antibodies and immune checkpoint inhibitors
Monoclonal antibodies are generally made in a laboratory in order to boost the body’s natural antibodies to fight against cancer. This also blocks the activity of abnormal proteins in cancer cells. It is known as targeted therapy, in which the medication is used to target the cancer’s tissues, genes, or proteins that help the cancer grow.
- Oncolytic virus therapy
Oncolytic virus therapy is also known as virus therapy, and it uses viruses that have been changed in a laboratory in order to destroy cancer cells. When the modified version of the virus is injected into the cancer cells, then it makes a copy of itself and damages the cancer cells. After the cells die, they release proteins that boost your immune system and target any cancer cells in your body.
- Cancer vaccines
A cancer vaccine exposes your immune system to a protein known as an antigen that helps to fight body disease. This boosts the immune system to destroy the antigen. To prevent cancer, there are two types of vaccine, i.e., prevention vaccines and treatment vaccines.
- T-cell therapy
T cells are the cells that help fight against infection. In T-cell therapy, a specialist removes T cells from the patients’ blood and adds proteins known as receptors to the cells. These receptors help to recognize cancer cells. The modified T cells are inserted into the body and then destroy cancer cells. This is also called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Why do People with a Healthy Immune System Get Cancer?
People with a healthy immune system suffer from cancer because the immune system doesn’t recognize the cancer cells as these cells aren’t different from normal cells. Secondly, the immune system recognizes the cancer cells, but they are not strong enough to destroy the cancer. And cancer cells produce substances that keep the immune system from attacking them. Hence, researchers have found ways so that the immune system can recognize cancer cells and destroy them.
The Side-effects of Immunotherapy
The various side-effects of immunotherapy are fatigue, nausea or vomiting, mouth sores, diarrhea, high blood pressure, fever, pain or weakness, headaches, and itching.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy boosts your immune system and helps fight cancer. This therapy stops cancer cells from growing in the patient’s body. Immunotherapy alone can be helpful to treat cancer and in combination with chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy, A cancer treatment that uses the immune system of a patient to fight cancer. Immunotherapy treatment can alter how the immune system functions to detect and destroy cancer cells and improve their functioning.
Types of Immunotherapy for cancer treatment
There are many types of immunotherapy for cancer. The most common is the non-specific immunotherapy, which boosts the immune system and allows the body to attack cancer cells. Other forms of immunotherapy involve laboratory-modified viruses that either kill cancer cells or alert the immune system to attack them.
One form of immunotherapy for cancer is monoclonal antibodies. This treatment uses an immune protein, called a monoclonal antibody, to attack the antigens on cancer cells. The effect is similar to that of chemotherapy, but patients are left with fewer side effects. The immune system is able to kill more cancer cells with targeted therapy, and cancer patients are more likely to have remissions after receiving this type of treatment.
The most recent type of treatment, called oncolytic virus therapy, involves injecting a virus into the body to fight cancer cells.
The first oncolytic virus, Talimogene laherparepvec, was approved by the FDA in 2006. This oncolytic virus attacks cancer cells while sparing normal cells. Another type of immunotherapy uses substances that help the immune system fight cancer. These include cytokines, interleukin, and interferons. Some people receive the treatment by injection, but most people experience a low response rate.
Side-effects of immunotherapy
While immunotherapy for cancer is relatively inexpensive, it does have some side effects. Because the immune system works against cancer cells, it may attack healthy tissues, which is not beneficial for the patient’s health. The severity of side effects depends on the type and stage of cancer, the type of cancer, and the immunotherapy dose. Your health and overall health before starting treatment will determine whether immunotherapy is right for you or not. It is recommended that you follow your doctor’s instructions and consult your healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of these side effects.
Although there are some side effects associated with immunotherapy, some people may respond well to it. While some people experience side effects, others do not. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about the potential side effects and benefits of the treatment before making any decisions. The decision to try immunotherapy for cancer is an important part of your treatment, and your cancer specialist can discuss the specifics with you. It is also important to remember that it is not the best option for everyone.
Your cancer specialist will be able to discuss the risks and benefits of the treatment with you. It would help if you also were sure to report any side effects as soon as they occur. There are some tests before and after the treatment, but new side effects may develop months or even years after you begin.
As the immune system tries to attack the cancer cells, it may produce side effects. While these side effects are common, they are not life-threatening.
Oncoplus Hospital, being the top cancer hospital with best oncologists in Delhi can help you with a second opinion about immunotherapy