How Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Lung Cancer: A Growing Concern
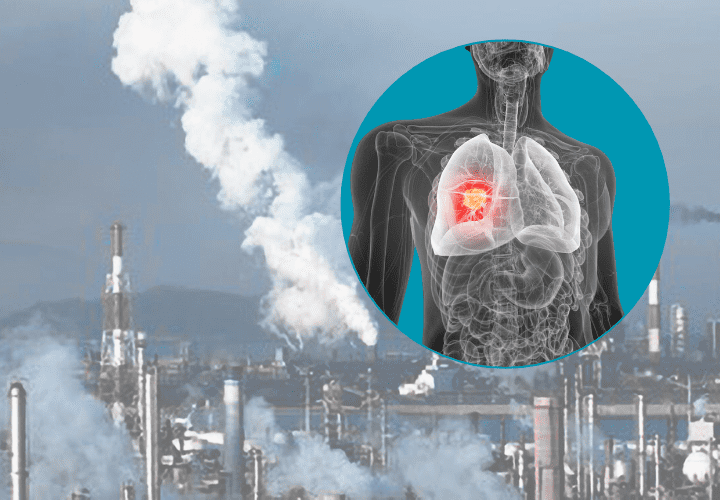
How Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Lung Cancer: A Growing Concern
- onco
- February 18, 2025
Air pollution is a major environmental issue affecting millions worldwide. It not only contributes to climate change but also poses serious health risks. Among these, lung cancer is one of the most alarming concerns. With rising industrialization, urbanization, and vehicle emissions, air pollution has reached hazardous levels. But how exactly does air pollution increase the risk of lung cancer? This article explores the dangerous connection between polluted air and lung cancer while offering ways to reduce exposure and protect your health.
Understanding Air Pollution
Air pollution consists of harmful substances in the air that negatively impact human health and the environment. These pollutants can be particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and heavy metals. The most dangerous pollutants linked to lung cancer are fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and toxic gases.
Types of Air Pollutants That Increase Lung Cancer Risk
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10) – These tiny particles penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to inflammation and DNA damage.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) – Emitted from burning fossil fuels, PAHs can cause genetic mutations that lead to cancer.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) – Commonly released from vehicles and industrial activities, NO2 increases oxidative stress in lung cells.
- Heavy Metals (Arsenic, Cadmium, Chromium, and Nickel) – These toxic substances, often found in polluted air, contribute to lung tissue damage.
The Link Between Air Pollution and Lung Cancer
- Cellular Damage and DNA Mutations
Air pollutants, especially PM2.5 and PAHs, penetrate lung tissues, causing oxidative stress. This stress leads to inflammation and DNA mutations, increasing the risk of uncontrolled cell growth—one of the main causes of cancer.
- Chronic Inflammation and Lung Damage
Continuous exposure to air pollution results in chronic inflammation in the respiratory tract. This prolonged inflammation damages lung cells, creating an environment where cancer cells can thrive.
- Suppressed Immune System
Polluted air weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight against abnormal cell growth. A compromised immune response allows cancerous cells to multiply unchecked.
- Increased Free Radicals
Exposure to air pollution significantly raises free radical levels in the body. Free radicals cause oxidative damage to lung tissues, which can lead to cancer development over time.
Who Is Most at Risk?
While air pollution affects everyone, certain groups are more vulnerable:
- Urban Dwellers – People living in cities with high traffic and industrial emissions.
- Children and Elderly Individuals – Their respiratory systems are more sensitive to pollutants.
- Smokers and Passive Smokers – Air pollution combined with smoking multiplies lung cancer risk.
- Industrial and Construction Workers – Those exposed to hazardous dust and chemicals at work.
Global Statistics and Research Findings
Recent studies have highlighted the alarming link between air pollution and lung cancer:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies outdoor air pollution as a Group 1 carcinogen.
- A study published in The Lancet Oncology found that exposure to PM2.5 increases lung cancer risk by 36%.
- According to the Global Burden of Disease Report, air pollution caused 1.8 million lung cancer deaths worldwide in 2021.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Exposure
Although air pollution is a global issue, individuals can take steps to minimize their risk of lung cancer:
- Reduce Outdoor Exposure
- Stay indoors during high pollution days and use air quality monitoring apps.
- Avoid heavy traffic areas where pollution levels are highest.
- Wear an N95 mask when pollution levels are high.
- Improve Indoor Air Quality
- Use air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove harmful pollutants.
- Keep indoor plants like peace lilies and snake plants, which absorb toxins.
- Avoid smoking indoors and reduce the use of aerosol sprays.
- Support Cleaner Energy Sources
- Switch to electric vehicles (EVs) or public transport to reduce emissions.
- Advocate for renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Encourage industries to adopt eco-friendly technologies.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Eat an antioxidant-rich diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen lung function.
- Get regular health check-ups to detect any lung abnormalities early.
Government Policies and Global Initiatives
Many governments and organizations are taking steps to combat air pollution and its health effects:
- The Paris Agreement aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions globally.
- Countries like India and China have introduced National Clean Air Programs to curb pollution.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) provides air quality guidelines to help nations develop policies.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a silent killer, contributing significantly to the rising cases of lung cancer worldwide. The increasing pollution levels have also led to a higher demand for cancer treatment in Delhi, where advanced medical facilities provide specialized care for lung cancer patients. Understanding the risks and taking preventive measures can help individuals safeguard their health. Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to reduce air pollution and create a healthier future. Prioritizing clean air today will save millions of lives tomorrow.
Recent Posts
-
Pap Smear Screening for Cervical Cancer: Everything You Need to Know
February 26, 2025

Leave a Reply