Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the liver cells. Several types of cancers can develop in the liver but Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver, which begins in the liver cell (hepatocyte).
Symptoms
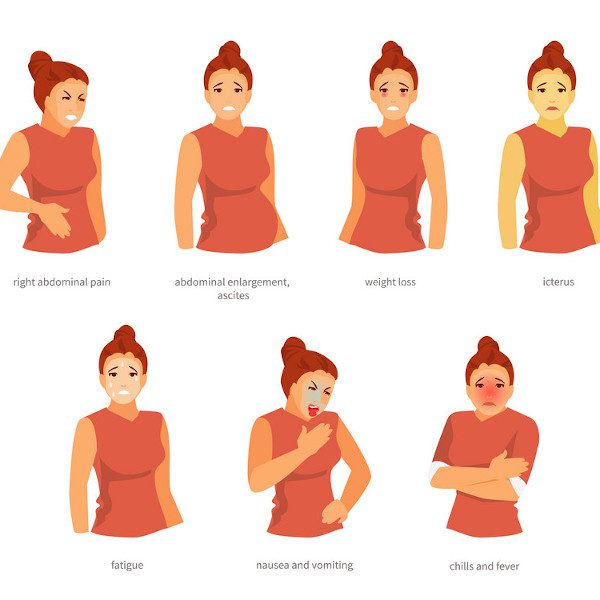
Symptoms of liver cancer do not appear until the cancer is at an advanced stage. But when signs and symptoms appear, these may include:
- Fatigability and general weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in the upper abdominal region
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swelling in Abdomen
- Jaundice leading to yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes
- White or chalky stools
Book an appointment with the Best Cancer Specialist at Oncoplus Hospital.
Causes and risk factors
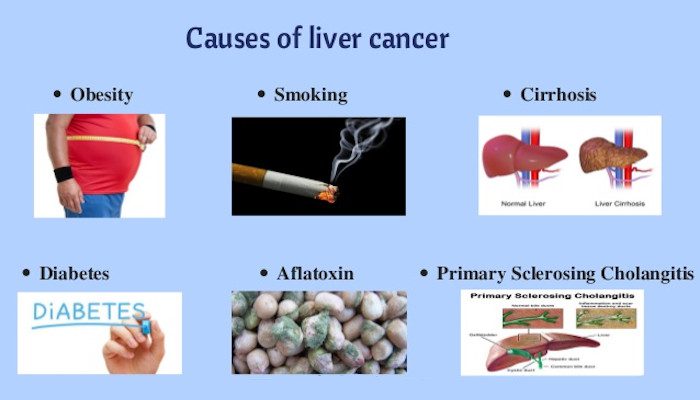
Hepatocellular Carcinoma or Primary liver cancer tends to occur in the liver because of the following:
- Birth defects
- Hemochromatosis – A hereditary disease associated with too much iron in the liver
- Obesity
- Chronic infection with Hepatitis B or C
- Cirrhosis. This condition is progressive and irreversible, causes scar tissue to develop in the liver increasing the chances of developing cancer in the liver.
- Certain inherited liver diseases including hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
- Diabetes. People with diabetes are at more risk of liver cancer than those who do not have diabetes.
- Fatty liver disease. Accumulation of fat in the liver increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
- Excessive alcohol consumption over many years may lead to liver damage increases the risk of liver cancer.
Diagnosis/screening
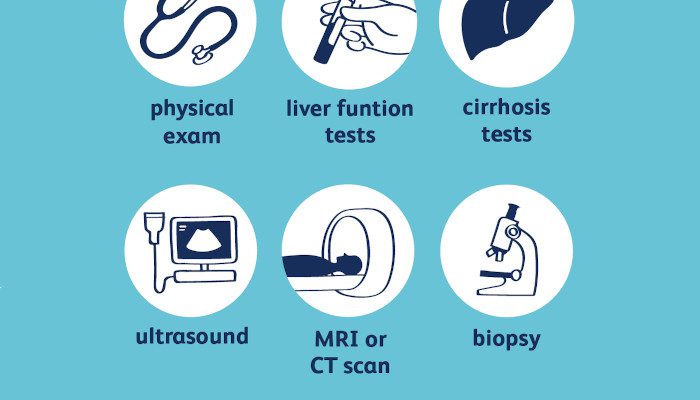
When someone shows signs and symptoms related to liver cancer, he/she should visit the physician for a general check-up. If the cancer is diagnosed in early stage, treatment is likely to be effective.
- Blood Tests
- Ultrasound
- CT Scan shows the exact location of cancer in the liver.
- MRI Scan
- Biopsy: The surgeon removes a sample of live tissue and examines it under a microscope to check for cancerous cells.
Book an appointment with the best oncologists for liver cancer treatment as well as a diagnosis at the best cancer Hospital in Delhi.
Stages
The staging of liver cancer determines the extent of cancer in the liver and body. After confirmation of the diagnosis, oncologists look for the stage of cancer. Certain tests including CT scans, MRIs, and bone scans help to determine the size and location of cancer and to what extent it has spread.
There are five stages in liver cancer:
Stage 0 – In this stage, the tumor is less than 2cm in size, and the liver functions normally.
Stage A – In this stage, the liver works well but tumor size increases up to 3 cm or there are a few small tumors less than 3cm in diameter develop in the liver.
Stage B – At this stage, multiple tumors are developed in the liver, but the person shows no signs and symptoms, as liver function is normal.
Stage C – At this stage, the cancerous cells have spread up to blood vessels, lymph nodes and the person is not feeling very well and is less active.
Stage D – This stage is advanced as a person experiences liver damage and needs urgent medical attention.
Cancer Treatment
The plan of treatment for liver cancer depends on certain factors such as the stage of the disease as well as the patient’s age, overall health. Treatment options for liver cancer are :
1. Surgery
- Surgical resection
Surgical resection is a term used for the procedure done to remove the cancerous cells if the liver is damaged partially limiting cancer in a small part of the liver. Since the liver can regenerate itself, that is the reason that it is possible to remove a large section of it without seriously affecting the health, but in the case of liver cancer, the ability of the liver to regenerate is impaired so surgical resection may be unsafe.Surgical resection can be performed or not is decided by the Oncosurgeons after a thorough assessment of the patient. - Surgery to remove the tumor. In cases where the tumor is small in diameter and the liver is functioning normally, in those cases, a small portion of healthy liver tissue surrounding the tumor is also removed along with the cancerous tissue.
- Liver transplant surgery. This surgery is by replacing the diseased liver with a healthy liver received from a donor. Liver transplant is done if:
- The single tumour is less than 5 cm in size
- The single tumour is up to 7 cm in size but has not grown for 6 months
- Three or a few small tumors less than 3 cm in size
2. Localized treatments
Localized treatments means treatments that are directly administered to the cancer cells. A few localized treatment options available for liver cancer are as follows:
- Radiofrequency ablation or heating the cancer cells. In this process, electric current is used to heat and destroy cancer cells in the liver.
- Cryoablation or Freezing cancer cells. Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the cancer cells eventually destroying the cancer cells.
- Injecting alcohol directly into the tumor either through the skin or during a surgical procedure. Alcohol kills the tumor cells.
- Radiation in the liver. beads filled with radiation may be placed directly in the liver where they can deliver radiation directly to the tumor-killing them
3. Radiation therapy
This treatment uses high-powered energy to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. Radiation therapy might be an option if other treatments are not possible or if they have not responded well.
4. Targeted drug therapy
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.
5. Immunotherapy
The cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells not letting the immune system fight cancer. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process, uses our immune system to fight cancer.
6. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses certain medicines to kill rapidly growing cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs are administered through a vein or orally.
7. Palliative Care or Supportive care
Palliative care is specialized medical care that aims on providing relief from pain due to some serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with the patient and the patient’s family to provide extra support complimenting the ongoing treatment and care.