Immunotherapy Drug – A Promising Treatment to Lower the Risk of Bladder Cancer Recurrence after Surgery:
Bladder cancer is a common malignancy that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the challenges in treating bladder cancer is the high risk of recurrence, even after surgical removal of the tumor. However, recent advancements in cancer treatment have shown promising results in reducing the risk of bladder cancer returning after surgery. One such breakthrough is the use of immunotherapy drugs, which have shown great potential in lowering the risk of bladder cancer recurrence and improving patient outcomes. If you or your loved ones are battling cancer, you can treat your different types of cancer at different stages with the help of the finest Immunotherapy in Delhi, India. Here in this blog, we will discuss how immunotherapy treatment lowers the risk of bladder cancer and its advantages.
Immunotherapy treatment lowers the risk of bladder cancer:
Bladder cancer is often treated with surgery, which involves removing the tumor from the bladder. However, even after the successful surgery, there is a high risk of cancer cells remaining in the bladder, leading to the recurrence of the disease. This is where Immunotherapy comes into play. It is a type of cancer treatment that works by harnessing the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
Read More Blog: Immunotherapy For Cancer Treatment In Delhi
One Immunotherapy drug that has shown remarkable success in lowering the risk of bladder cancer recurrence is pembrolizumab, which belongs to a class of drugs known as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Pembrolizumab works by blocking a protein called PD-1 in immune cells, which helps to activate the immune system and enhance its ability to identify and destroy cancer cells. By doing so, pembrolizumab helps to prevent cancer cells from evading the immune system’s detection and attack, reducing the risk of cancer recurrence after surgery.
Researchers have conducted multiple clinical trials to assess the effectiveness of pembrolizumab in reducing the risk of bladder cancer recurrence following surgery. One notable trial is the KEYNOTE-045 trial, which involved patients with advanced bladder cancer who had undergone surgery to remove the tumor. The trial results showed that pembrolizumab significantly reduced the risk of cancer recurrence compared to standard chemotherapy, leading to improved overall survival rates.
In addition to pembrolizumab, other immune checkpoints inhibitors, such as nivolumab and atezolizumab, have also shown promising results in lowering the risk of bladder cancer recurrence after surgery. These drugs received approval for treating advanced bladder cancer and are currently undergoing clinical trials to explore their potential in reducing the risk of recurrence after surgery.
Positive aspects of Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy offers a notable advantage with its comparatively favorable safety profile when compared to traditional chemotherapy. Unlike chemotherapy, which often leads to adverse effects like nausea, hair loss, and immune suppression, immunotherapy drugs like pembrolizumab typically exhibit fewer side effects and are better tolerated by patients. This makes them a more attractive option for bladder cancer patients who have undergone surgery and are looking to lower their risk of recurrence without experiencing debilitating side effects.
Read More Blog: How Does Immunotherapy Help In The Fight Against Cancer?
Another advantage of immunotherapy is its potential to provide long-term benefits. Unlike chemotherapy, which is typically given in cycles, immunotherapy is often administered continuously, allowing for sustained immune system activation and cancer cell destruction. This prolonged effect may help to prevent the regrowth of cancer cells in the bladder and reduce the risk of recurrence over the long term.
It’s important to note that:
- Not all bladder cancer patients are eligible for immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is typically reserved for patients with advanced or metastatic bladder cancer, as well as those at a high risk of recurrence following surgery.
- Eligibility for immunotherapy is determined on a case-by-case basis by the patient’s oncologist, taking into consideration various factors such as the stage and type of bladder cancer, the overall health of the patient, and previous treatments received.
Immunotherapy drugs like pembrolizumab show promise in reducing bladder cancer recurrence after surgery. They harness the body’s immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells, preventing their spread. Clinical trials and real-world data support the efficacy of pembrolizumab and other immunotherapy drugs, especially for high-risk bladder cancer patients. Immunotherapy represents a significant advancement in oncology, providing a new approach to managing this complex disease. However, more research is required to optimize patient selection, dosing, and combination therapies to maximize the benefits of immunotherapy in bladder cancer treatment.
So if you want to resist cancer, look no further than Oncoplus, the leading cancer hospital in Delhi. Our state-of-the-art facility offers cutting-edge immunotherapy treatments that harness the power of the body’s immune system to fight cancer effectively. With a team of highly skilled oncologists and advanced technology, we provide personalized care and treatment plans for various types of cancer. Experience the latest advancements in cancer care at Oncoplus, where hope meets innovation. Contact us today to book a consultation and take a step towards a brighter tomorrow!
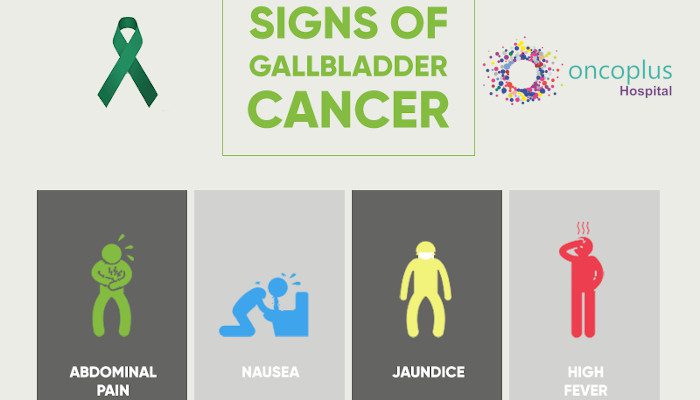
Gallbladder cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops in the gallbladder, a small organ located just beneath the liver. When carcinogenic or malignant cells start to proliferate abnormally and uncontrollably in the gallbladder, gallbladder cancer develops. The early stages of gallbladder cancer often do not cause any symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose. However, as the cancer progresses, it can cause a variety of symptoms that can be indicative of the disease.
It is commonly known that those who have already received treatment fear developing gallbladder cancer. Even after completing cancer therapy and emerging as a survivor, a cancer recurrence is possible. In this blog, we will discuss the 10 advanced-stage symptoms of gallbladder cancer that you should be aware of-
- Abdominal pain: As the cancer grows, it can cause pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. This pain can be dull or sharp and may radiate to the back or shoulder.
- Jaundice: The cancer can block the bile ducts, causing jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Nausea and vomiting: The cancer can also cause nausea and vomiting, often as a result of the blockage of the bile ducts.
- Loss of appetite: As the cancer progresses, it can cause a loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Fatigue: Cancer can cause fatigue, a feeling of exhaustion and weakness that is not relieved by rest.
- Itching: Cancer-related jaundice can cause itching all over the body.
- Abdominal swelling: As the cancer grows, it can cause abdominal swelling due to the build-up of fluid in the abdomen.
- Blood clots: Gallbladder cancer can cause blood clots, which can be life-threatening if they travel to the lungs.
- Bowel obstruction: The cancer can also cause a bowel obstruction, which can cause constipation, abdominal pain and vomiting.
- Metastasis: Advanced-stage gallbladder cancer can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, bones and brain. This can cause symptoms such as bone pain, headaches and difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it’s essential to see a doctor if you are experiencing any of them. A diagnosis of gallbladder cancer is made through a combination of tests, including an ultrasound, CT scan and biopsy.
Gallbladder cancer risk factors
The exact causes of gallbladder cancer are not well understood, but certain risk factors have been identified. These include-
Age: The risk of gallbladder cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 60.
Gender: The prevalence of gallbladder cancer is higher in women than in males.
Race: Gallbladder cancer is more common in people of Native American and Hispanic descent.
Gallstones: Having a history of gallstones increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can raise the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Chronic inflammation of gallbladder: Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can increase gallbladder cancer risk.
Family history: Having a family history of gallbladder cancer increases the risk of developing the disease.
It is also to note that exposure to certain chemicals, such as petrochemical, pesticides and a specific type of hair dyes, can also increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Treatment of Gallbladder cancer
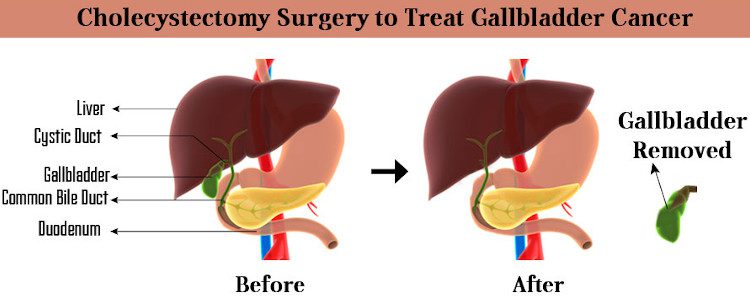
Gallbladder cancer treatment typically involves surgery to remove the gallbladder and surrounding tissue. In some cases, lymph nodes in the area may also be removed. In the advanced stages of the disease, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be used in addition to surgery. The treatment plan will be determined by the stage and progression of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Early diagnosis is key to the successful treatment of gallbladder cancer. It’s important to be aware of the symptoms of the disease and to see a doctor if you are experiencing any of them. If you have a family history of gallbladder cancer or other risk factors for the disease, such as gallstones or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, it’s essential to talk to your doctor about regular screenings.
Prevention of Gallbladder cancer
There are a few ways to reduce the risk factors of gallbladder cancer:
Maintaining a healthy diet and weight: Obesity is a risk factor for gallbladder cancer, so maintaining a healthy diet and diet can help reduce the risk.
Avoiding gallstones: Gallstones can cause inflammation in the gallbladder, which can increase the risk of cancer. Avoiding foods that are high in fat or cholesterol can help prevent gallstones.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of gallbladder cancer.
Treating gallbladder disease: If you have gallbladder disease or gallstones, it’s essential to have them treated to reduce cancer risk.
Regular checkups: Regular checkups with your doctor can help detect any early signs of gallbladder cancer and increase the chances of successful treatment if the cancer is found.
It’s also important to note that certain inherited conditions, such as Lynch Syndrome, increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
In conclusion, Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious disease that can cause a variety of symptoms as it progresses. The most common symptoms of advanced-stage gallbladder cancer are abdominal pain, jaundice, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, itching, abdominal swelling, blood clots, bowel obstruction, and metastasis. It’s essential to be aware of these symptoms and to see a doctor if you are experiencing any of them. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis of gallbladder cancer. So if you experience any of the symptoms, you should consult with the best oncologist in Delhi, India.
What is gall bladder cancer?
Gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ placed on the right side of the abdomen, a bit below the liver. Its normally an inch in width and three to four inches long. It stores a digestive fluid called bile that is formed in the liver, which helps in digesting the fats. It is a helpful organ but not an important one, people live normally after getting their gall bladder removed. Gall bladder cancer is a very uncommon cancer, which originates in the tissues of gall bladder and is often identified late as there are no signs and symptoms in the initial stages. The exact reasons for gall bladder cancer are not known, though there are several risk factors, which increases the risk of gall bladder cancers.
Studies state that people between forty-five to sixty-five years of age are at risk. It is more prevalent among women in India, and gallstones remains the most common risk factor for gallbladder cancer, family history of gallstones doubles risk of gall bladder cancer. Being overweight too increases the risk of many types of cancers, including gall bladder cancer. Diet with increased intake of proteins, fats and cholesterol and meals low in fibre, vegetables and fruits has been suggested as a risk factor for Gall Bladder Cancer. If people have one or more risk factors, this doesn’t mean that people will get gall bladder cancer for sure. Numerous people with no exposure to risk factors also get cancer.
There is no certain way of preventing gall bladder cancers. We cannot control the risk factors such as age, gender, ethnicity and hereditary abnormalities. But we can always take precautions and adopt healthy living to reduce the risk factors such as obesity, doctors recommend to eat healthy and exercise often.
Include cereals, whole grains, at least two and half cups of vegetables and fruits daily in meals, limit intake of processed foods and red meat. Consult a cancer specialist if you experience abdominal pain, many people with gall bladder cancer have an aching feeling on the upper right part of the belly and experience lump in the abdomen. Rarer symptoms of gall bladder cancer includes loss of appetite, fever, and weight loss.
If you or your dear ones have any of these symptoms, consult our Cancer specialist at Oncoplus Hospital, Defence Colony, New Delhi without delay so that the cause can be diagnosed and treated, in time. Experts opine that surgery can’t cure gallbladder cancer, which has spread in other areas of the body. Clinicians use treatments, which may relieve signs and symptoms of cancer and make you as contented as possible, other treatment options include Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy, and Clinical trials. Tele Consult with our expert doctors at Oncoplus Hospital, Defence Colony, New Delhi, write to us info@oncoplus.co.in or call us at +91 85889 09091 to book an appointment and learn more about Gallbladder Cancer treatment.
Gallbladder cancer develops in the gallbladder, a tiny organ located under the liver, behind the lower right ribs. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile, which helps digest fats. High risk factors for gallbladder cancer are obesity and medical conditions that end up affecting the gallbladder, for instance gallstones, cysts or polyps. Women are twice as likely to develop this type of cancer than men.
Gallbladder cancer is rather rare, but when it does occur, it is largely diagnosed in its advanced stages. Gallbladder cancer can also prove to be difficult to diagnose, in part because the gallbladder is rather small and buried deep within the body, making tumours much harder to find. Also, the symptoms will not typically appear until the cancer has reached an advanced stage.
At Oncoplus, South Delhi’s best cancer hospital, we deploy a range of diagnostics and techniques to better diagnose and stage all cancer treatment and tailor customised cancer treatment plans for our patients’ needs. We also provide support and counselling that may help you manage the side effects of your treatment, so you can better maintain your strength, stamina and keep the quality of life you want to: throughout treatment.
We target and treat gallbladder tumours with highly sophisticated, evidence-backed treatment and technology. A multidisciplinary team of gallbladder cancer experts will answer all your questions and recommend the best cancer treatment options based solely on your unique diagnosis and needs.
The Common courses of treatment for gallbladder cancer include:
Surgery
Surgery is a common treatment for gallbladder cancer, and is used to remove the tumor or relieve symptoms. It may also be used to help alleviate pain if the cancer is more widespread.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used in addition to surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence or in cases where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Radiation therapy
Radiation may also be used after surgery or as a palliative treatment if the cancer has progressed.
Support and care
We understand managing the side effects of gallbladder cancer treatment is most critical to maintaining your quality of life. In addition to treating your cancer with evidence-based conventional approaches, our team will recommend various supportive care therapies designed to help you stay strong throughout treatment. They may include:
Nutritional support
Every patient has the option of meeting with a registered dietitian.
Pain management
Pain management is a branch of medicine focused on reducing pain and improving quality of life through an integrative approach to care.
Oncology rehabilitation
Oncology rehabilitation includes a wide range of therapies designed to help you build strength and endurance.